Python 3 package for illustrating crystallography
Python 3 package for illustrating crystallography
The miller indices are used to denote the planes in crystal lattices.
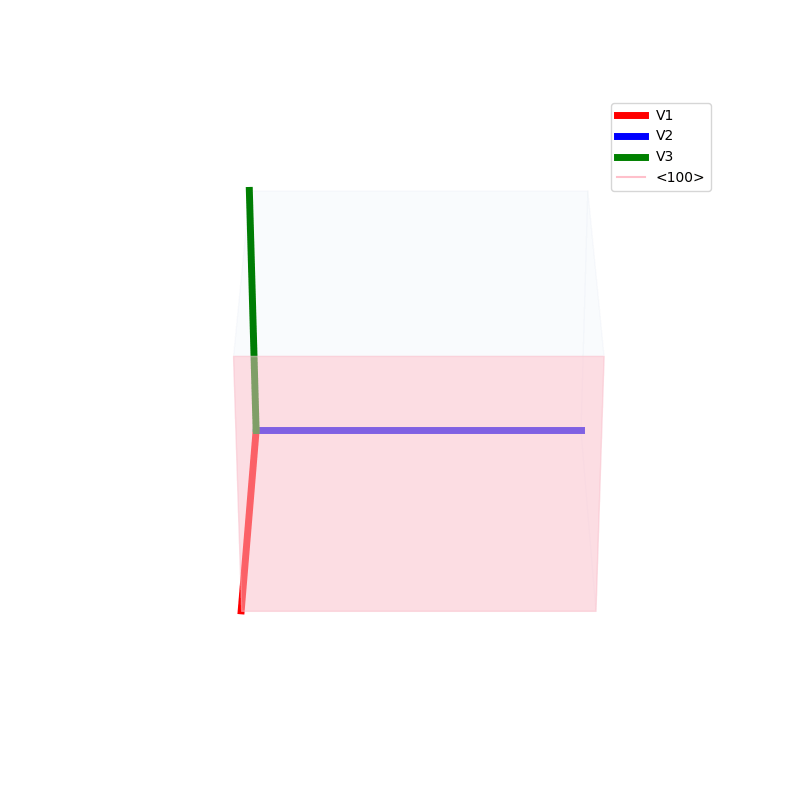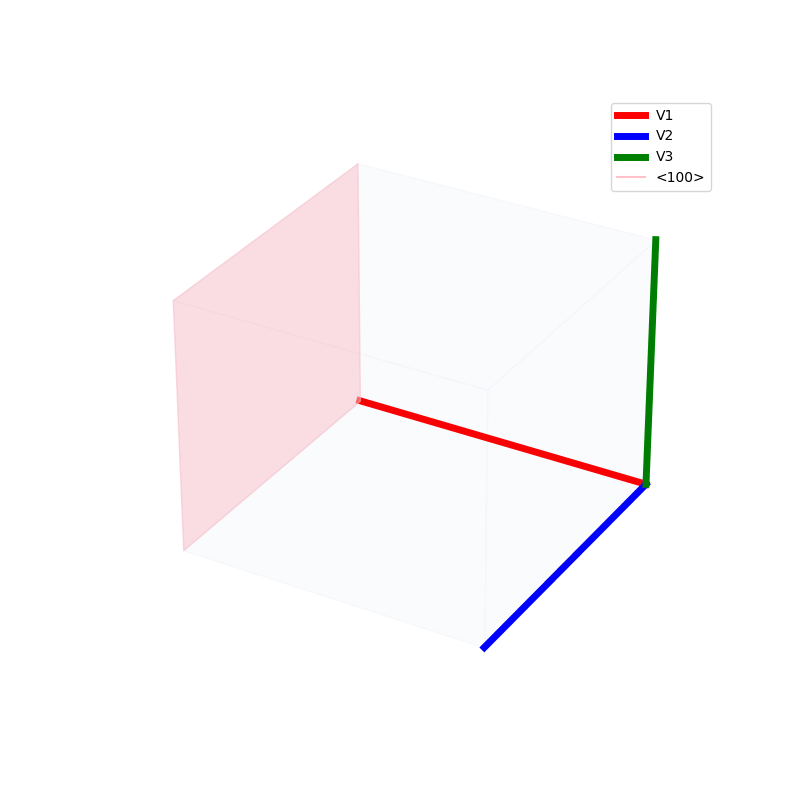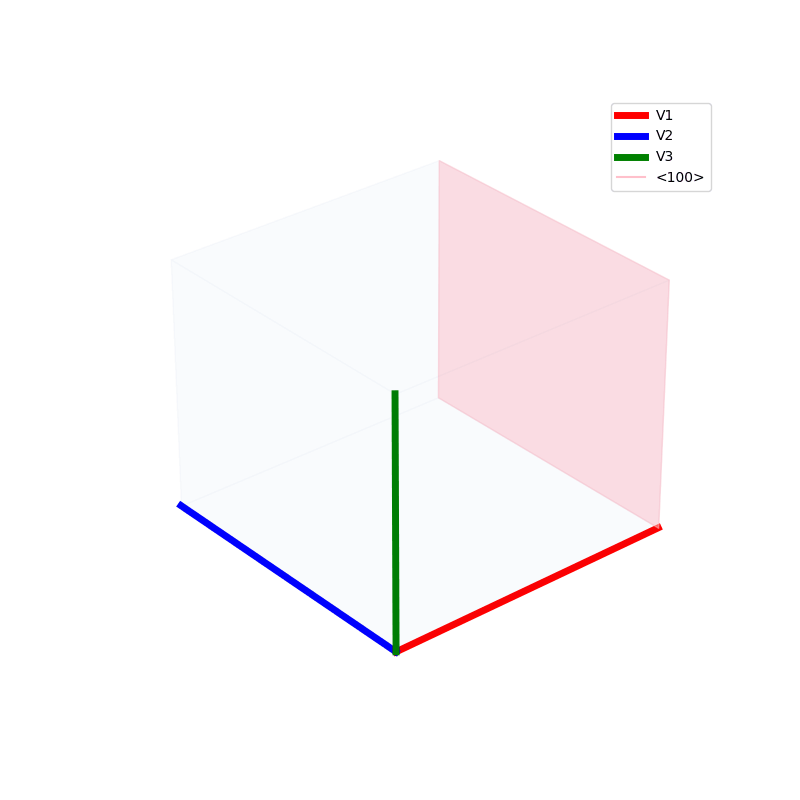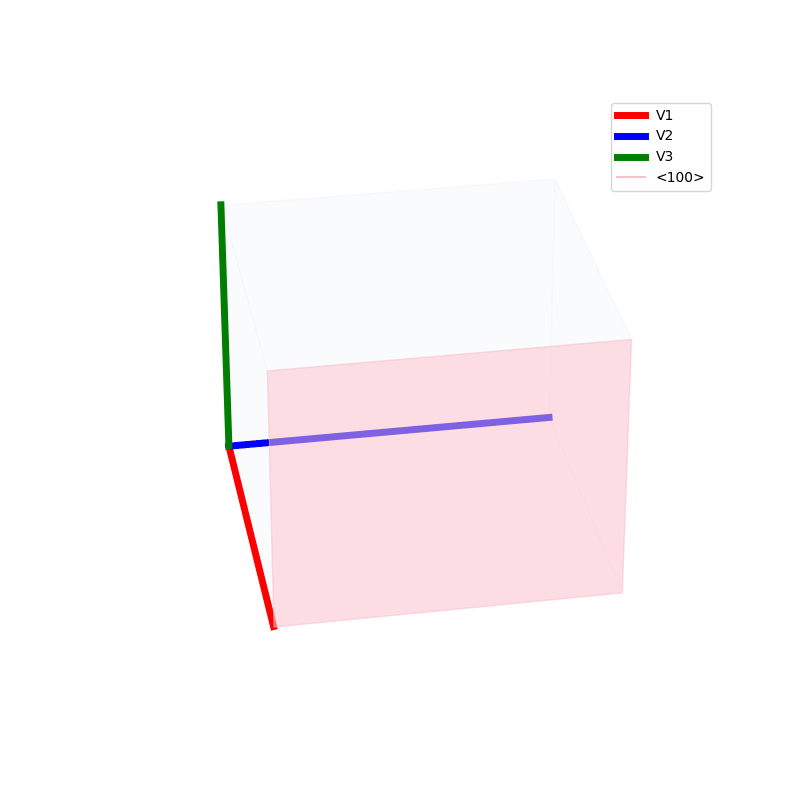
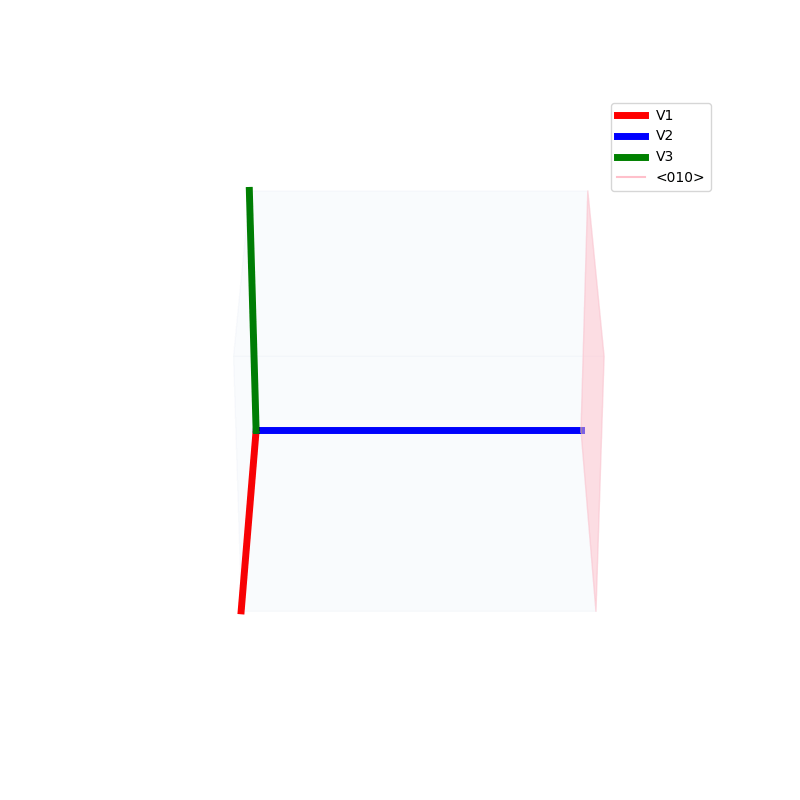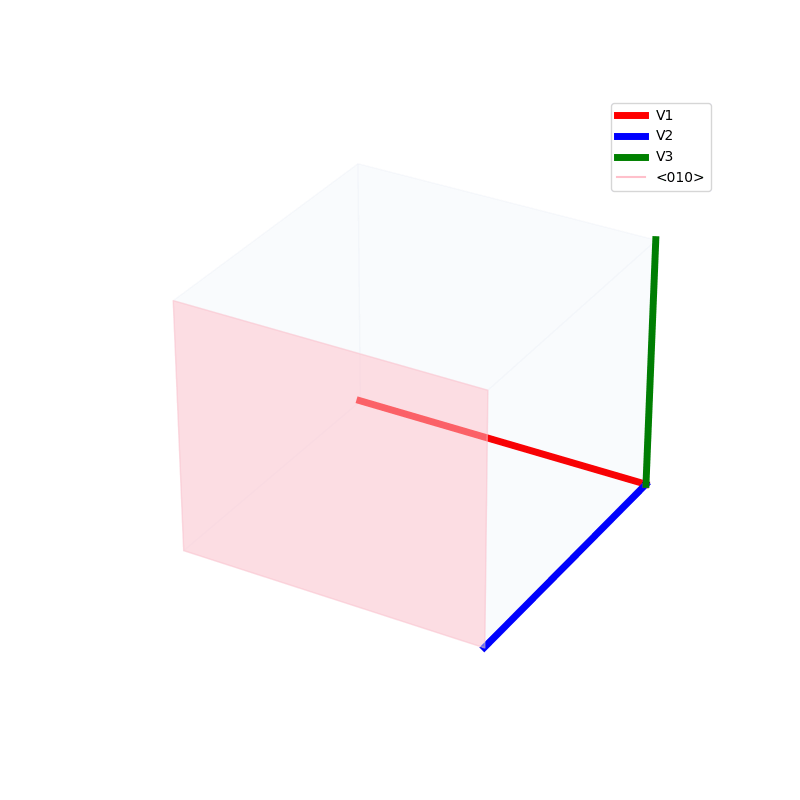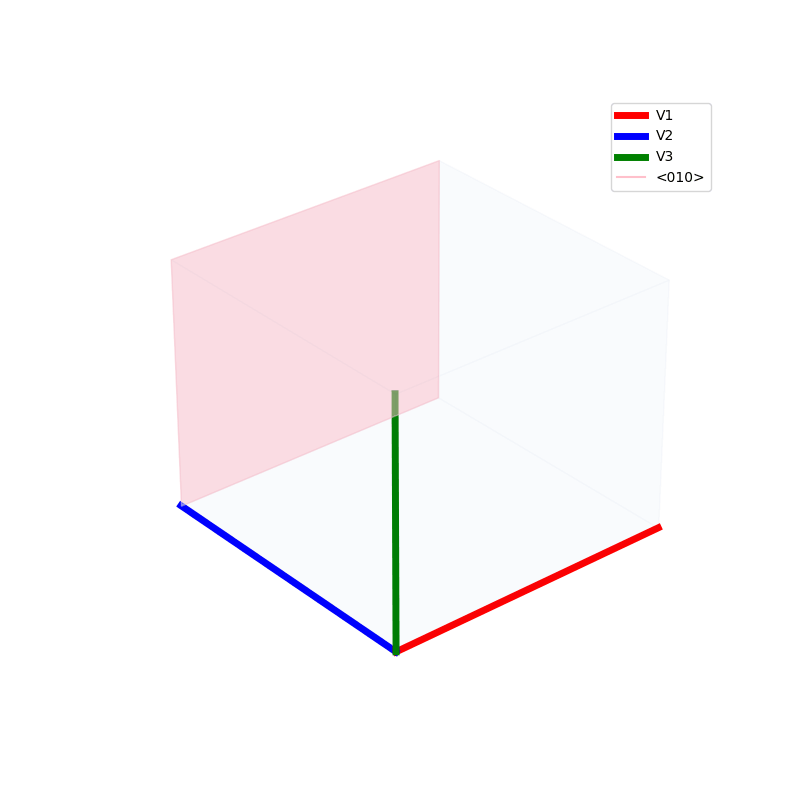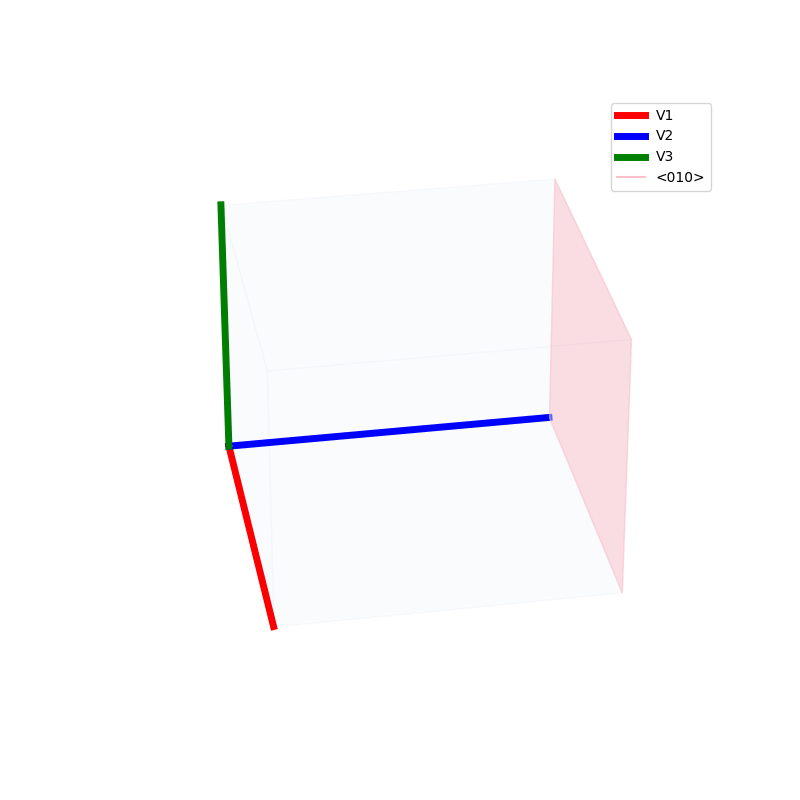
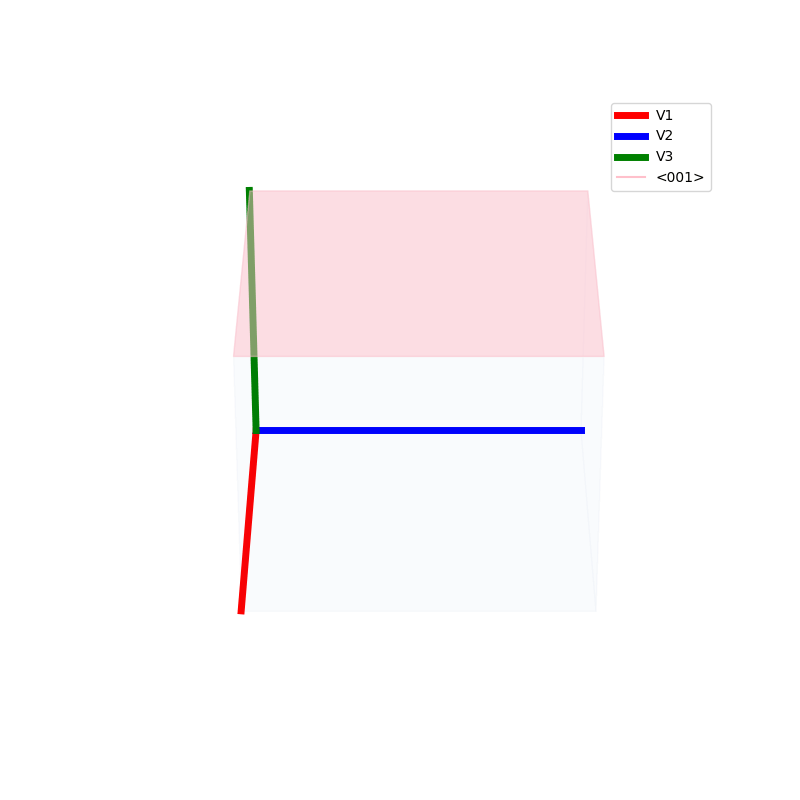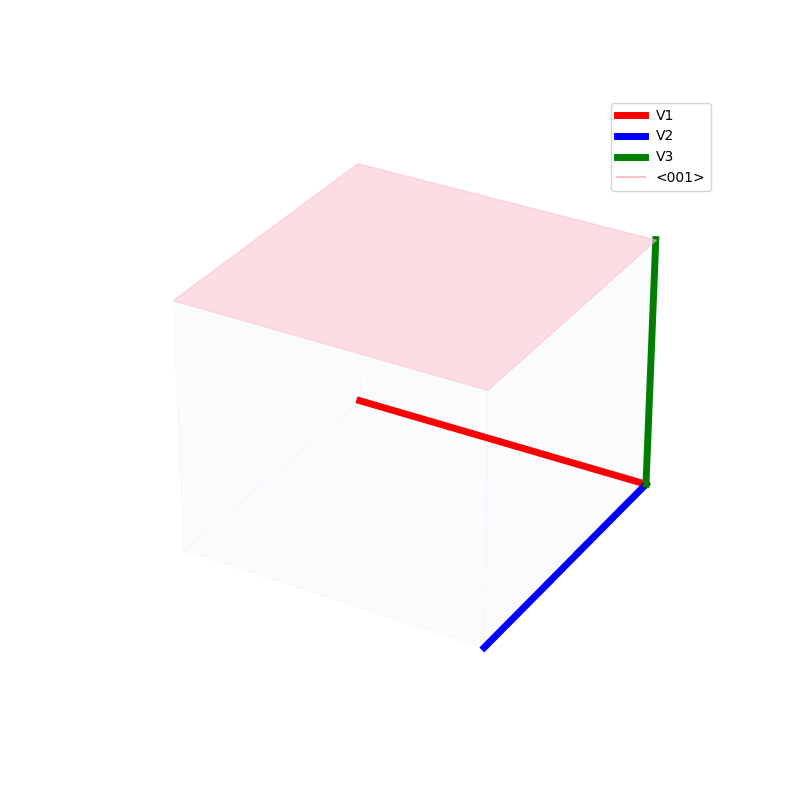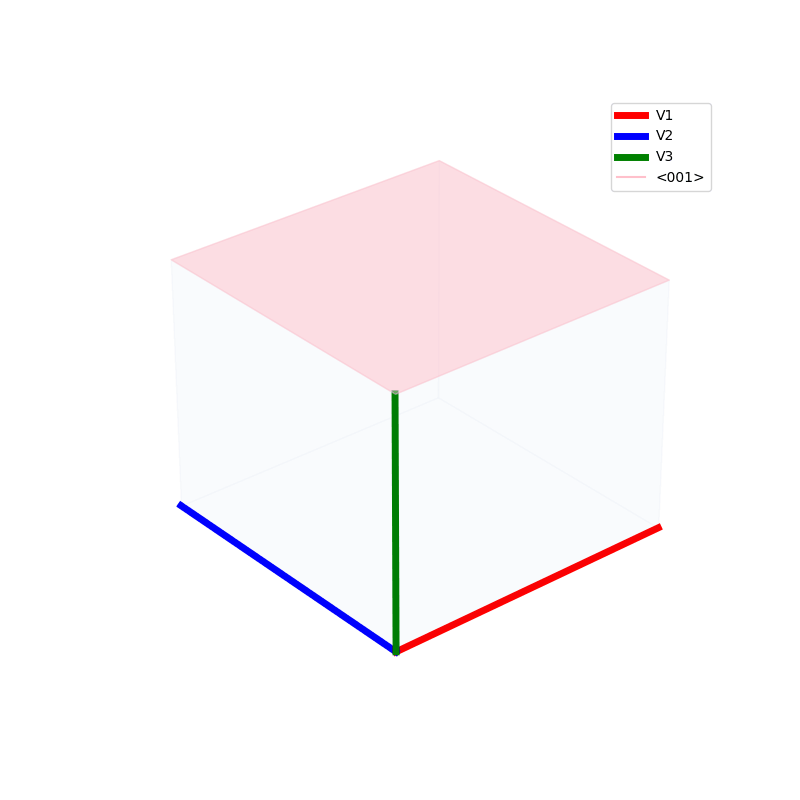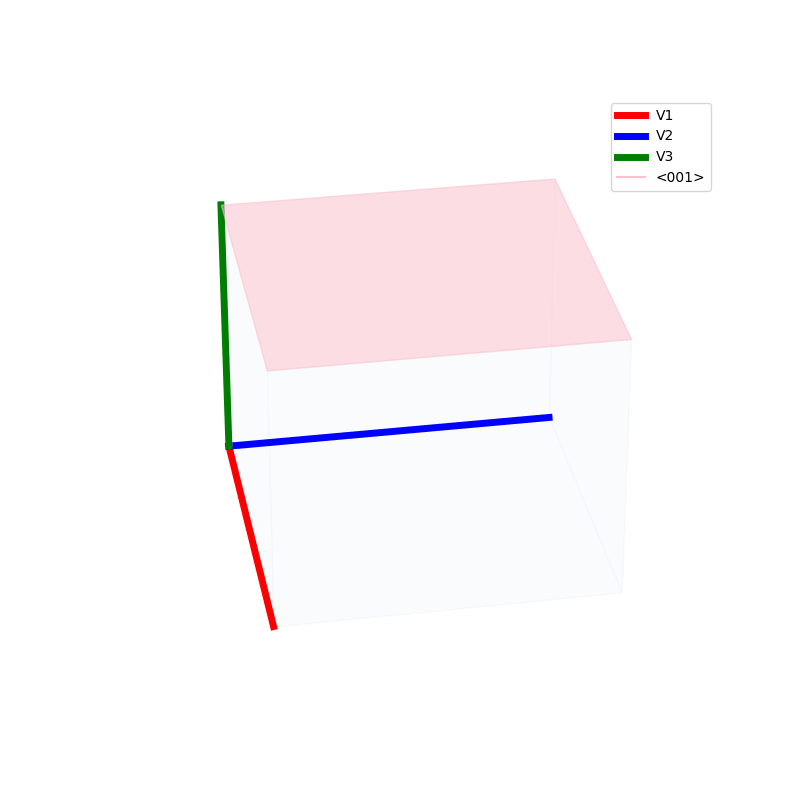

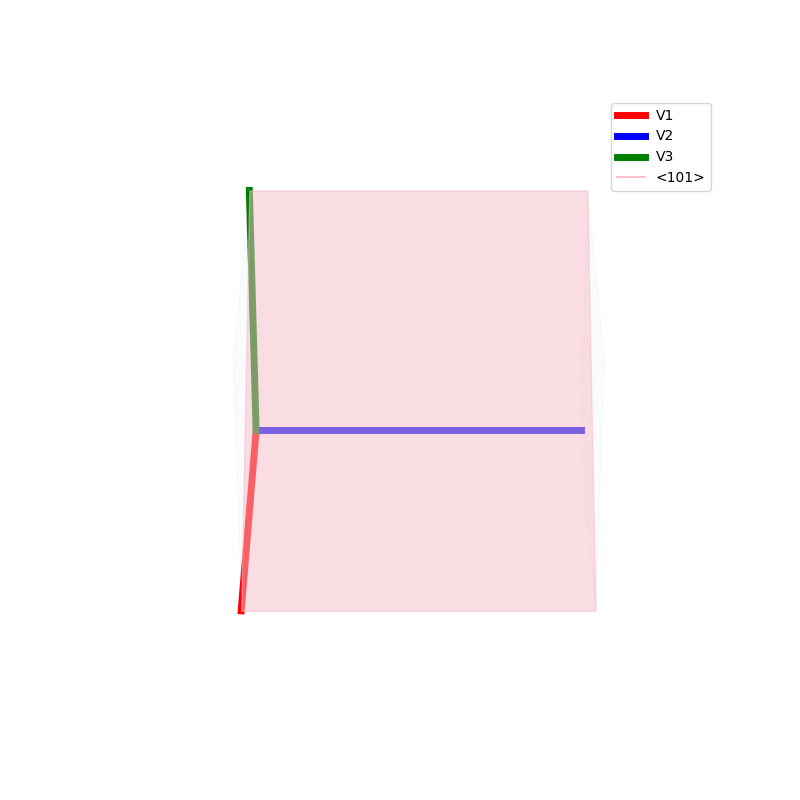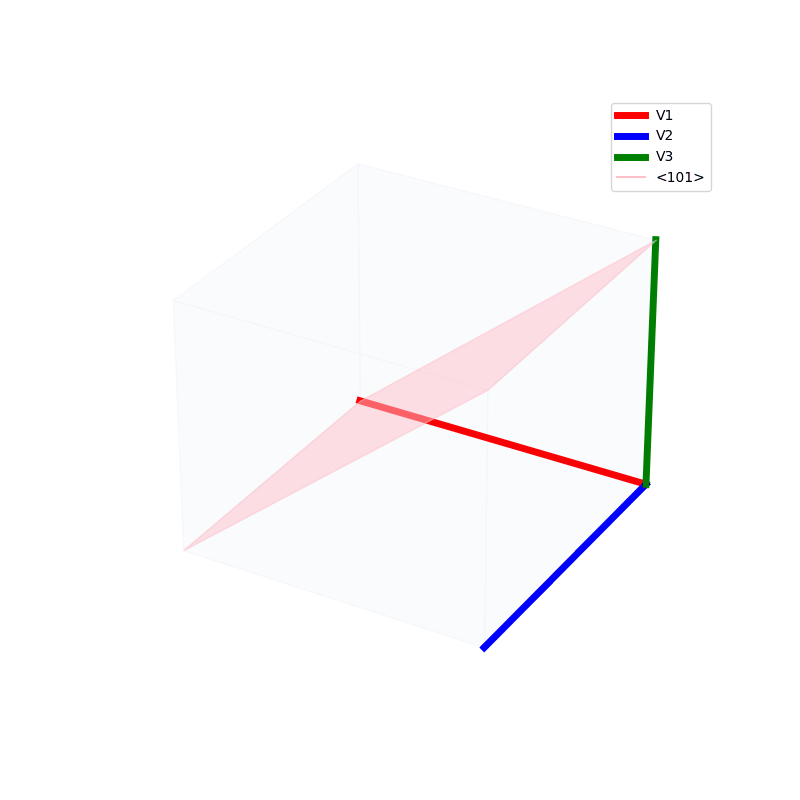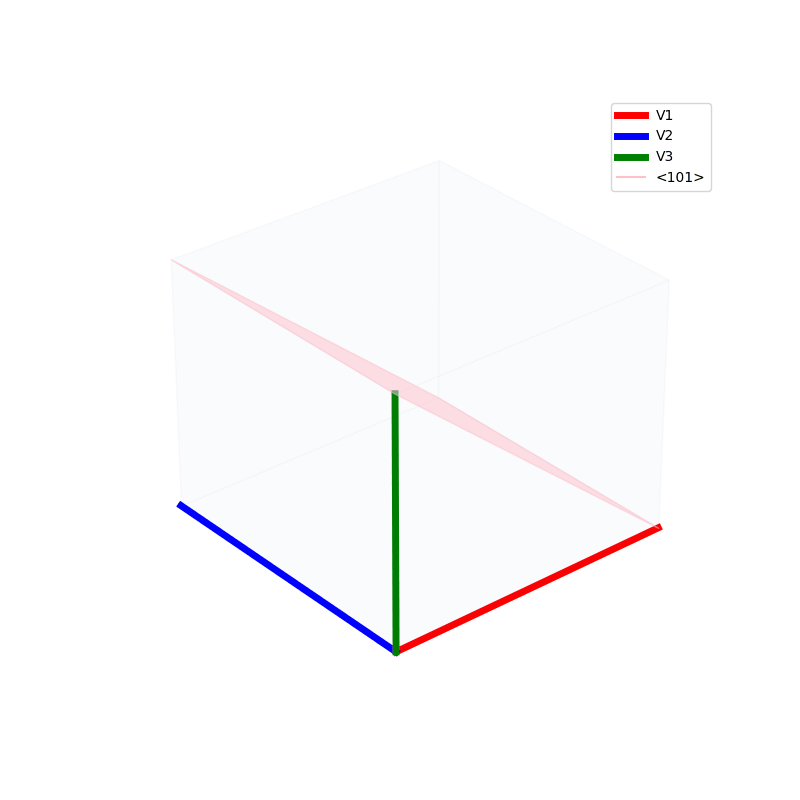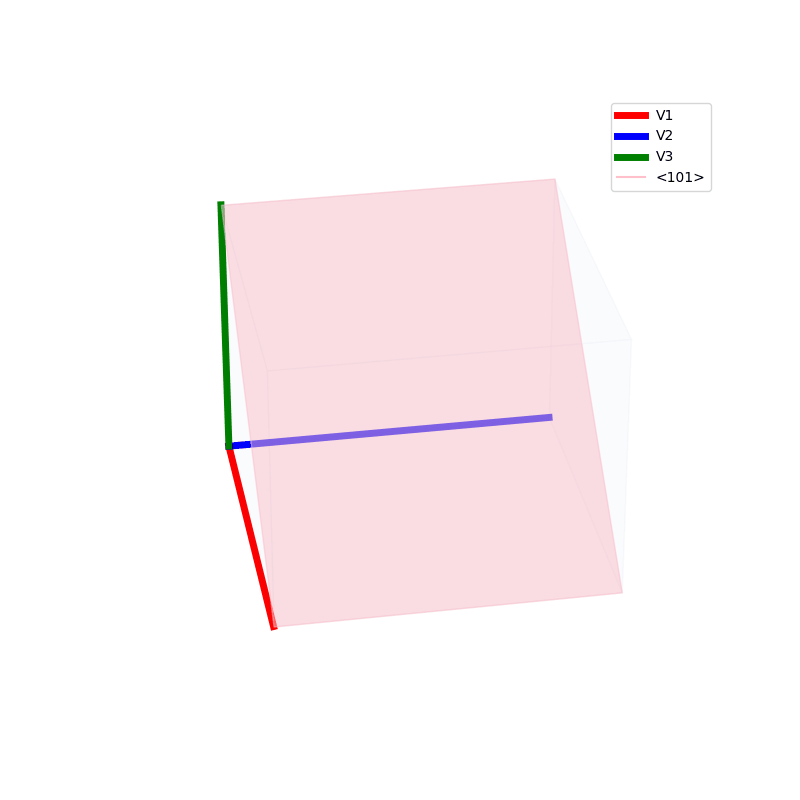

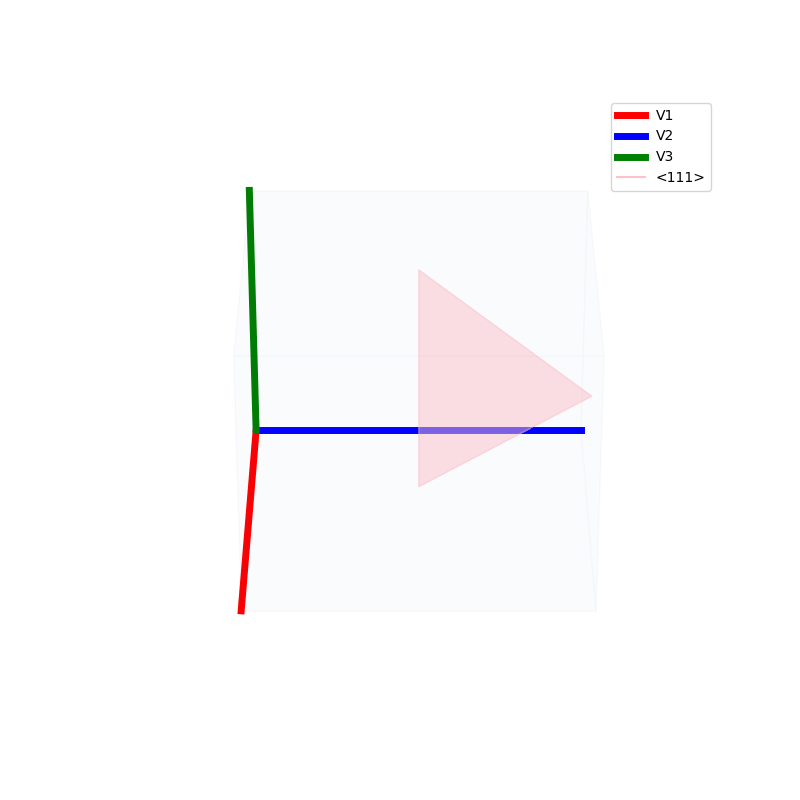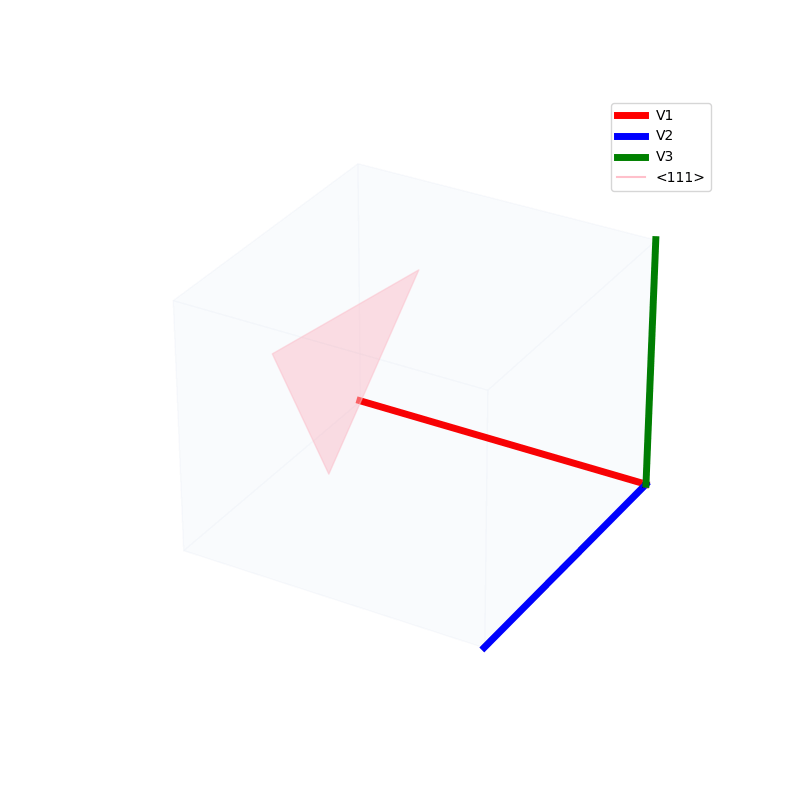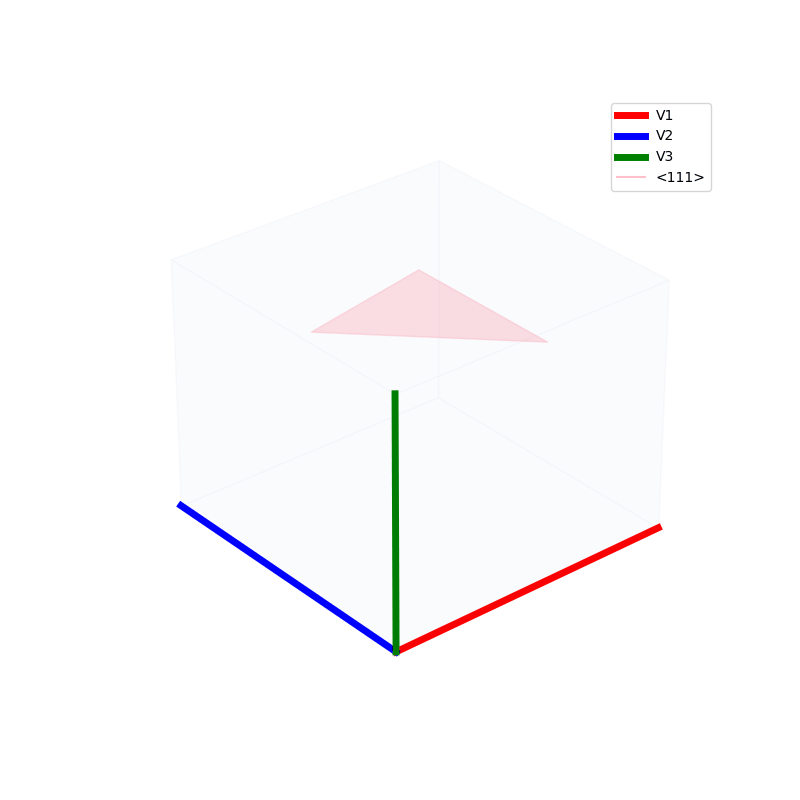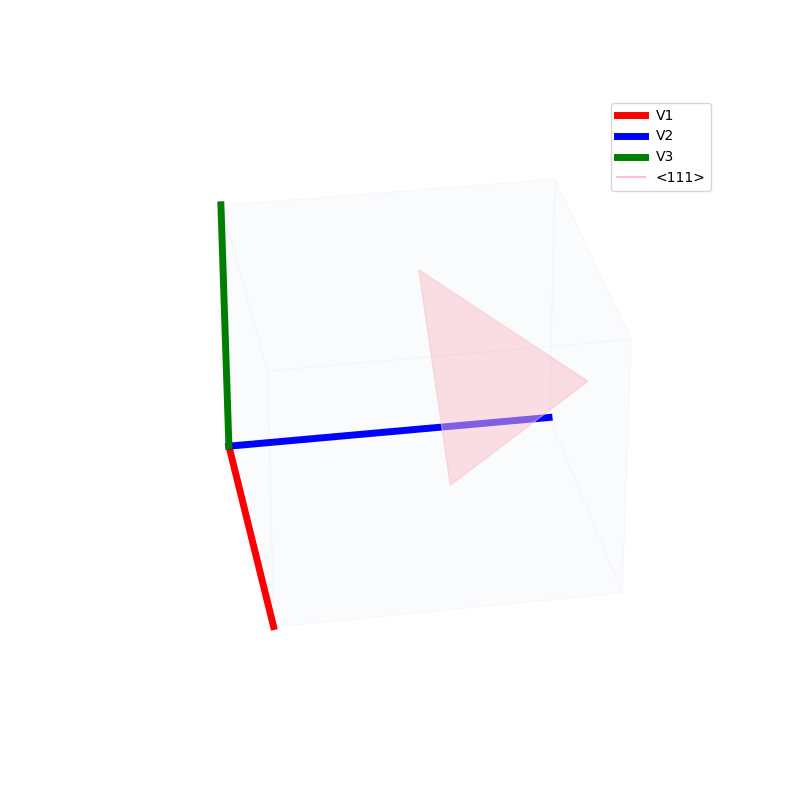
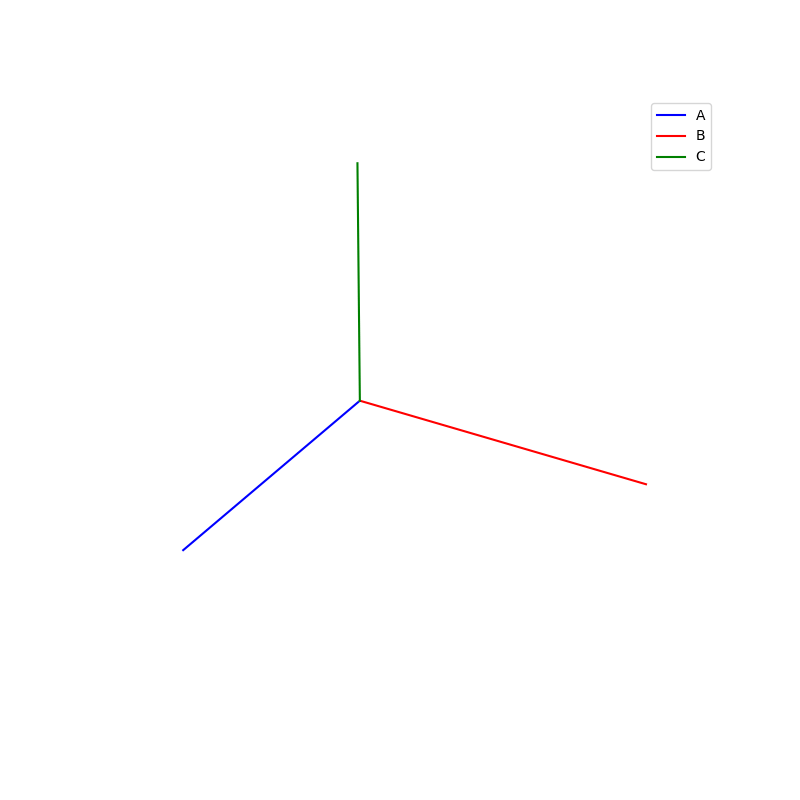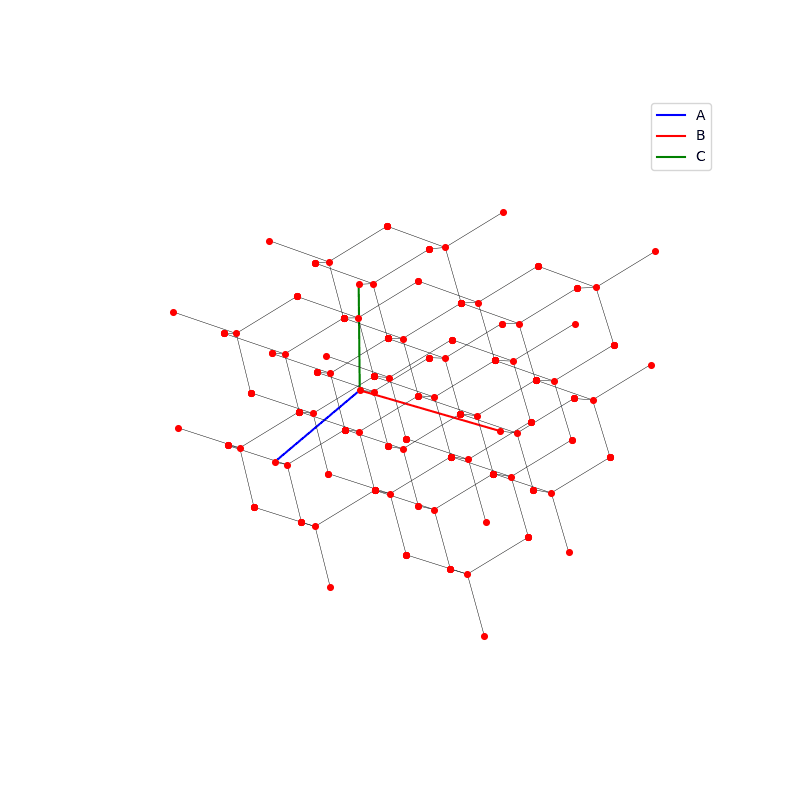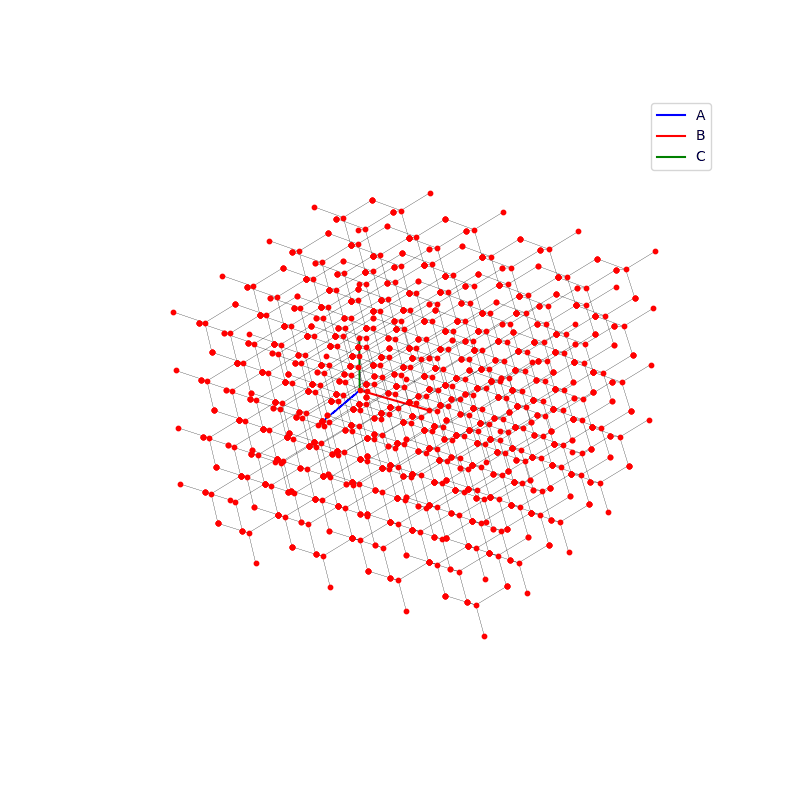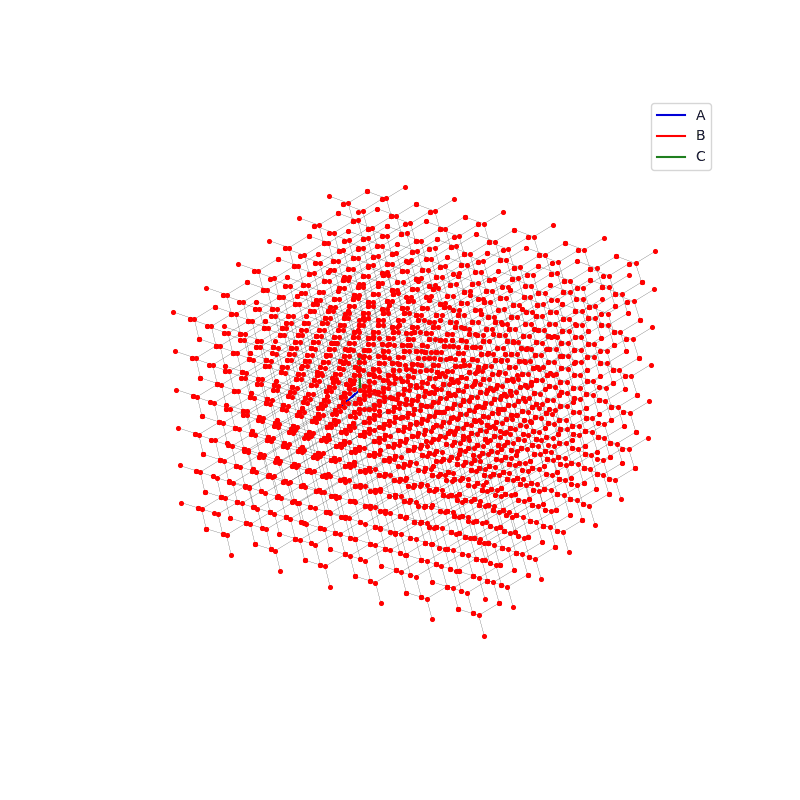
Lattices are used as a way to map the structure of crystals. A Bravais Lattice is on that is constructed from an infinite array of discrete points by a set of discrete translation operations (primitive vectors, A,B,C in the below figures.)
from PyCrystallography import unit_cell
prim = unit_cell.primitive_cell_2d('square')
from PyCrystallography import lattice
lattice.make_lattice(prim)
plt.show()
from PyCrystallography import unit_cell
prim = unit_cell.primitive_cell_2d('rhombus')
from PyCrystallography import lattice
lattice.make_lattice(prim)
plt.show()
possible unit cell shapes:
trianglesquarerhombushexagon




CODE:
from PyCrystallography import unit_cell
from PyCrystallography import lattice
import matplotlib .pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
#set lattice depths
d = 3
#set primitive vectors
A = [1,0,0]
B = [0,1,0]
C = [0,0,10]
vectors = [A,B,C]
fig = plt.figure('Latiices',figsize=[8,4])
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121,projection='3d')
ax1.set_title('Bravais')
prim = unit_cell.custom_unit_cell(ax1,vectors)
lattice.make_lattice_3d(ax1,prim,depth=d)
vectors_r = lattice.make_vectors_reciprocal(vectors)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122,projection='3d')
ax2.set_title('Reciprocal')
prim = unit_cell.custom_unit_cell(ax2,vectors_r)
lattice.make_lattice_3d(ax2,prim,depth=d,tag='_r')
plt.show()
OUTPUT:
Primitive Vectors
A = [1, 0, 0]
B = [0, 1, 0]
C = [0, 0, 10]
Unit Cell Volume = 10
Reciporocal Primitive Vectors
A_r = [6.28318531 0. 0. ]
B_r = [0. 6.28318531 0. ]
C_r = [0. 0. 0.62831853]
Reciprocal Unit Cell Volume = 24.805021344239854

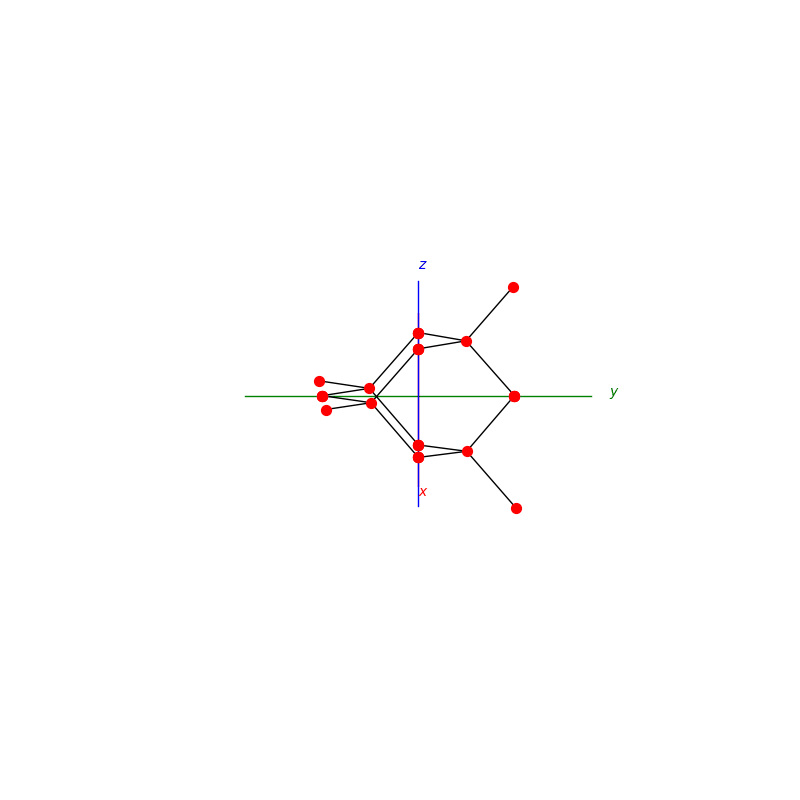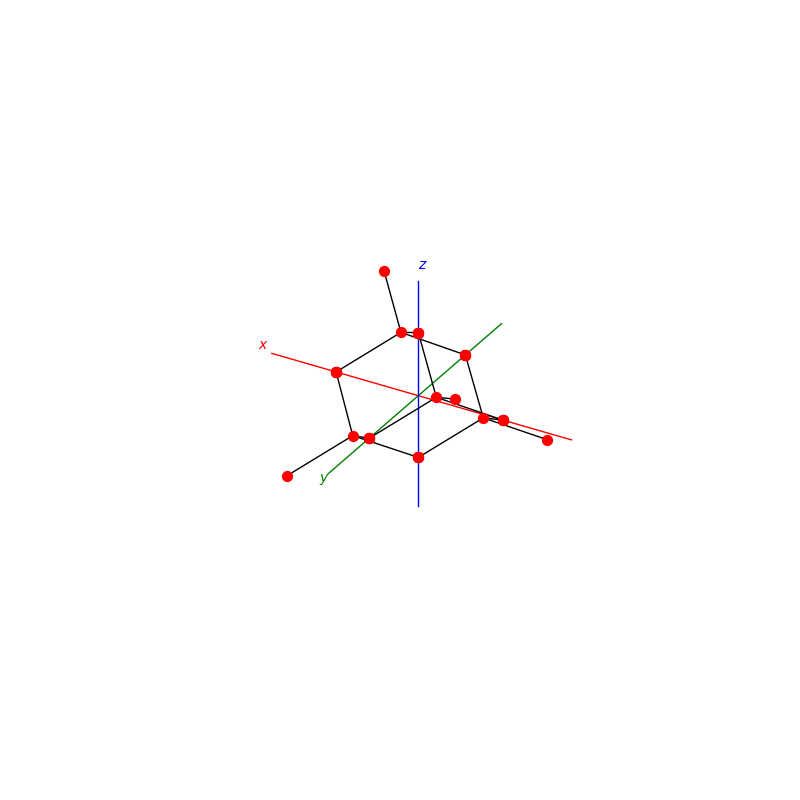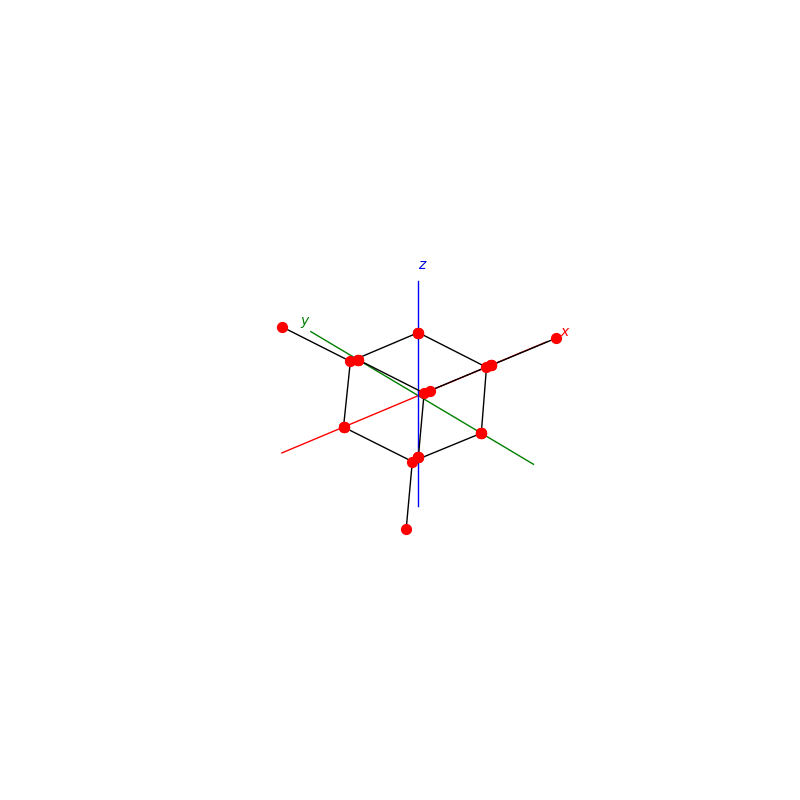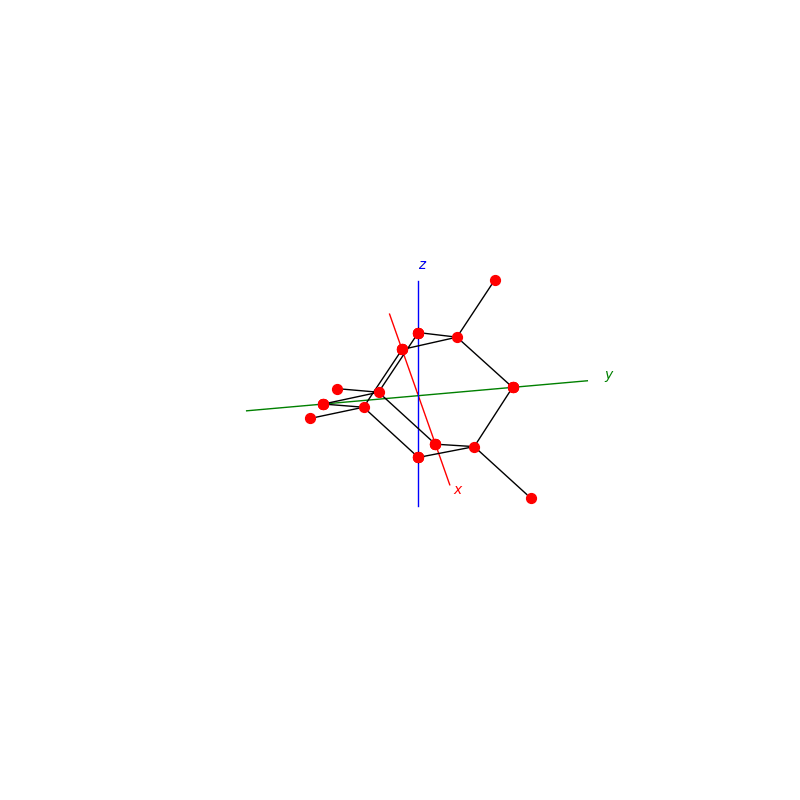
A lattice is made up of cells, the most important being primitive unit cells.
fig = plt.figure(0,figsize=[8,8])
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,projection='3d')
from PyCrystallography import unit_cell
prim = unit_cell.BCC(ax)
fig = plt.figure(1,figsize=[8,8])
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,projection='3d')
from PyCrystallography import lattice
lattice.make_lattice_3d(ax,prim)
plt.show()

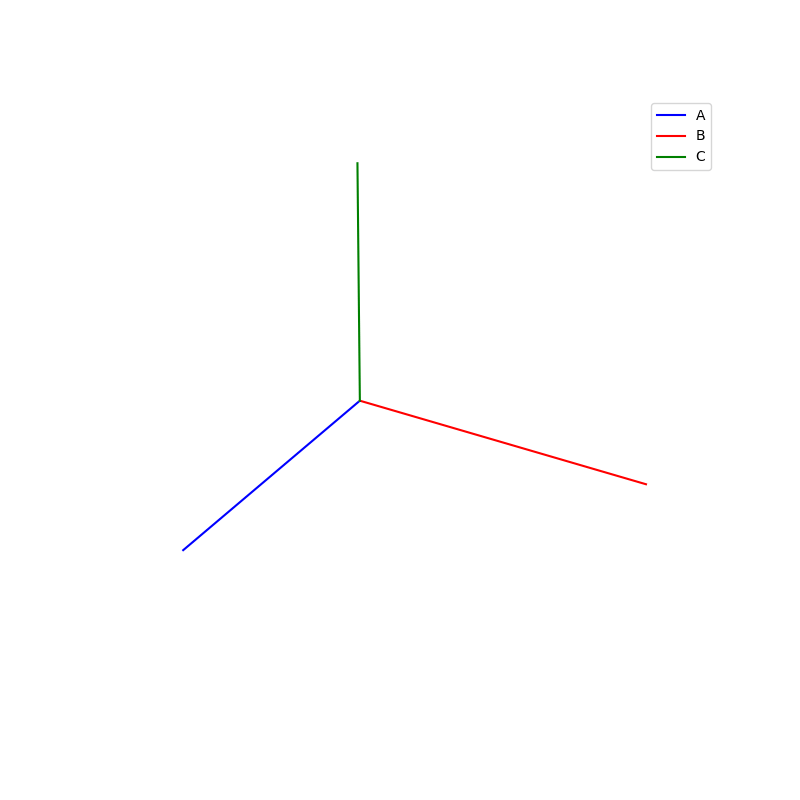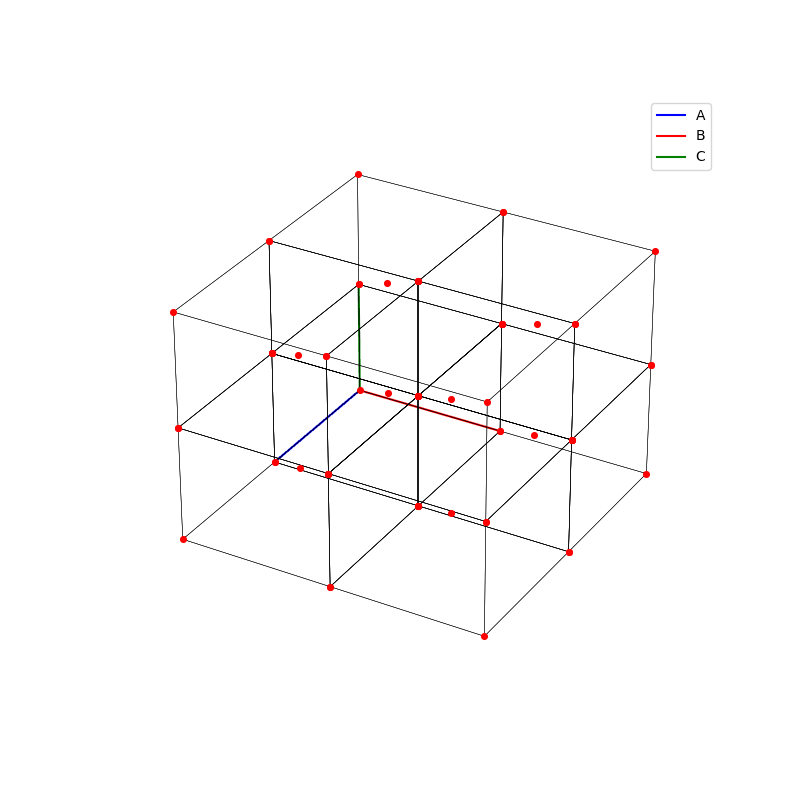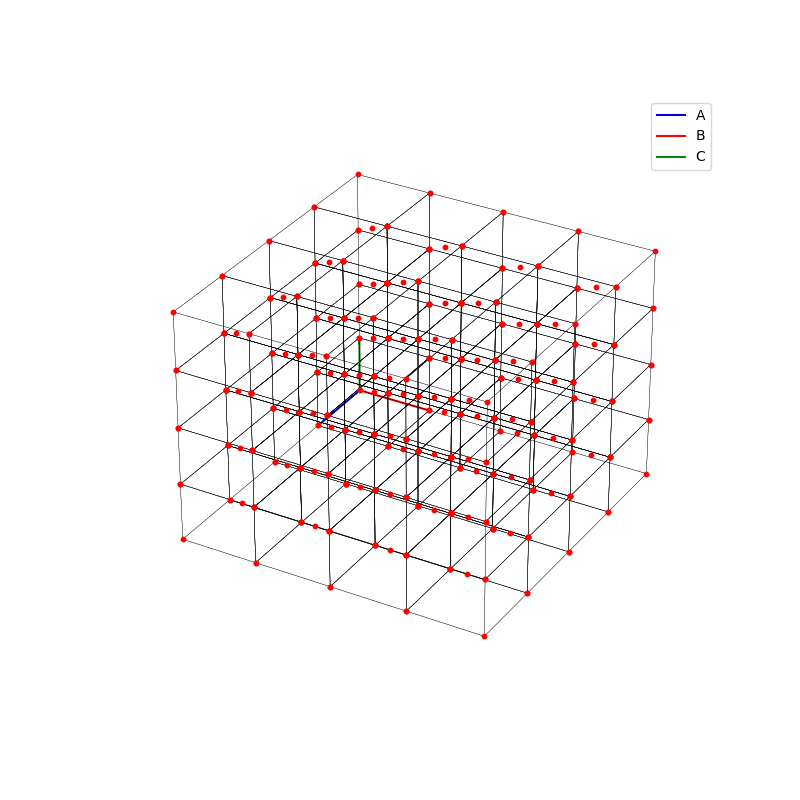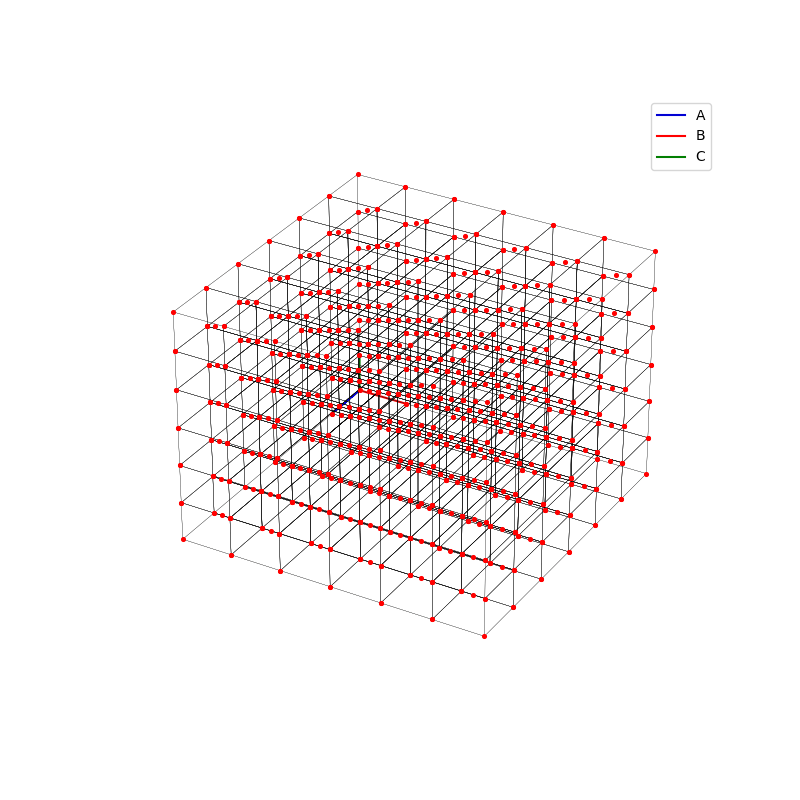
fig = plt.figure(0,figsize=[8,8])
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,projection='3d')
from PyCrystallography import unit_cell
prim = unit_cell.FCC(ax)
fig = plt.figure(1,figsize=[8,8])
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,projection='3d')
from PyCrystallography import lattice
lattice.make_lattice_3d(ax,prim)
plt.show()
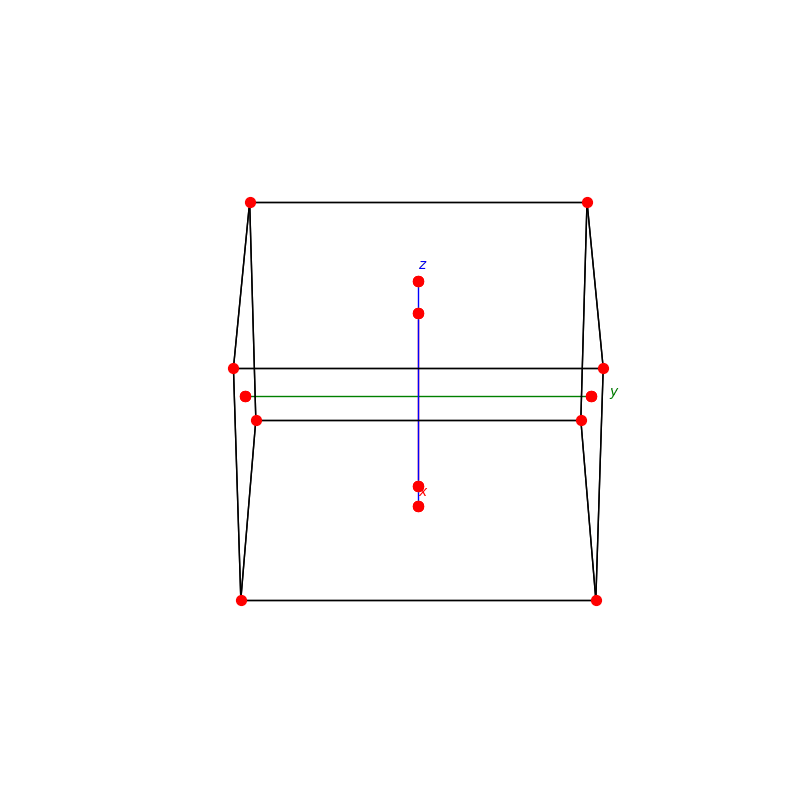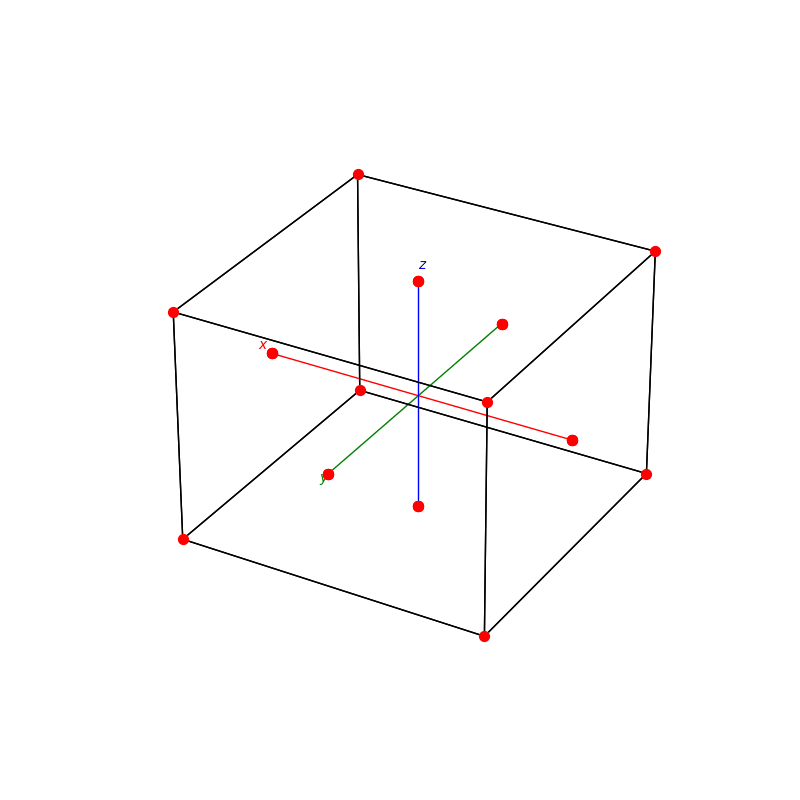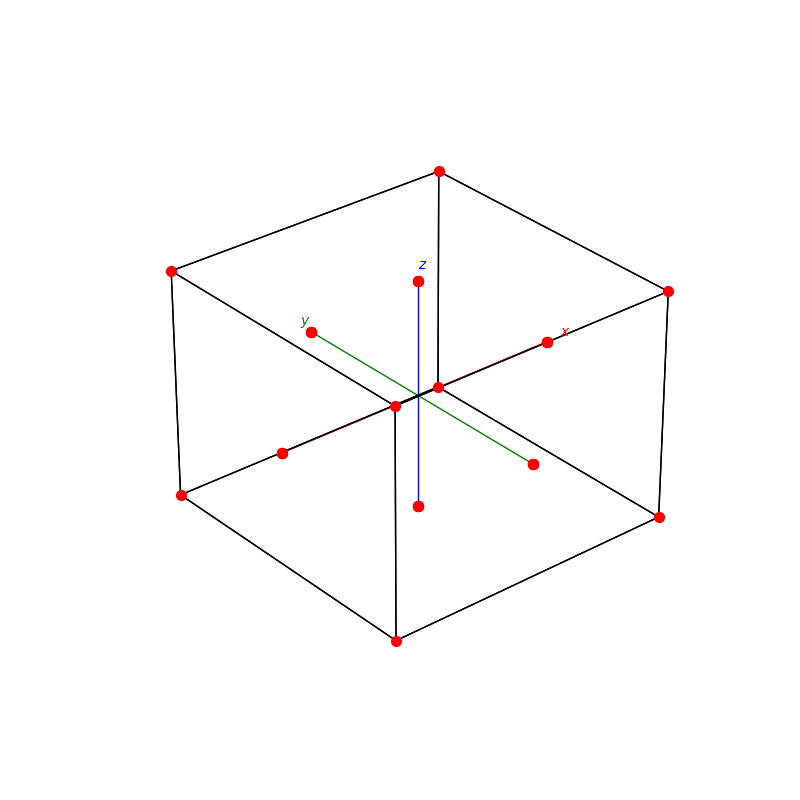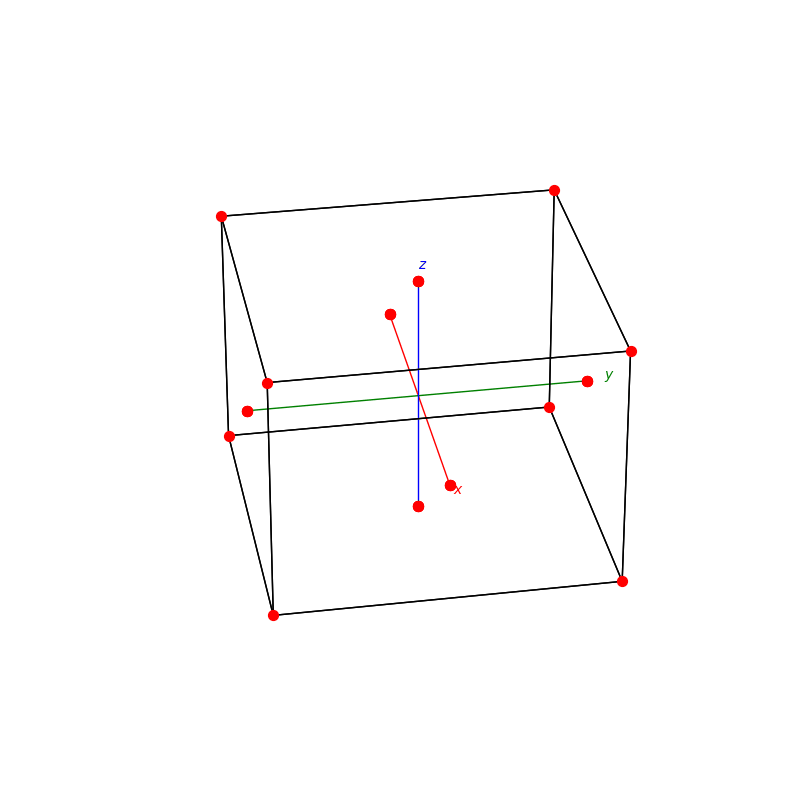
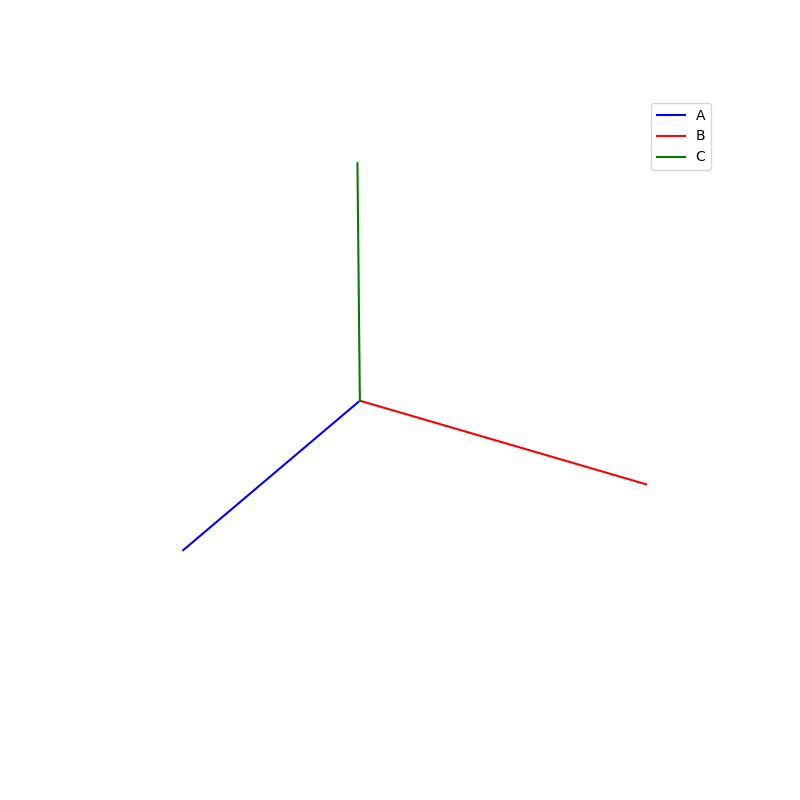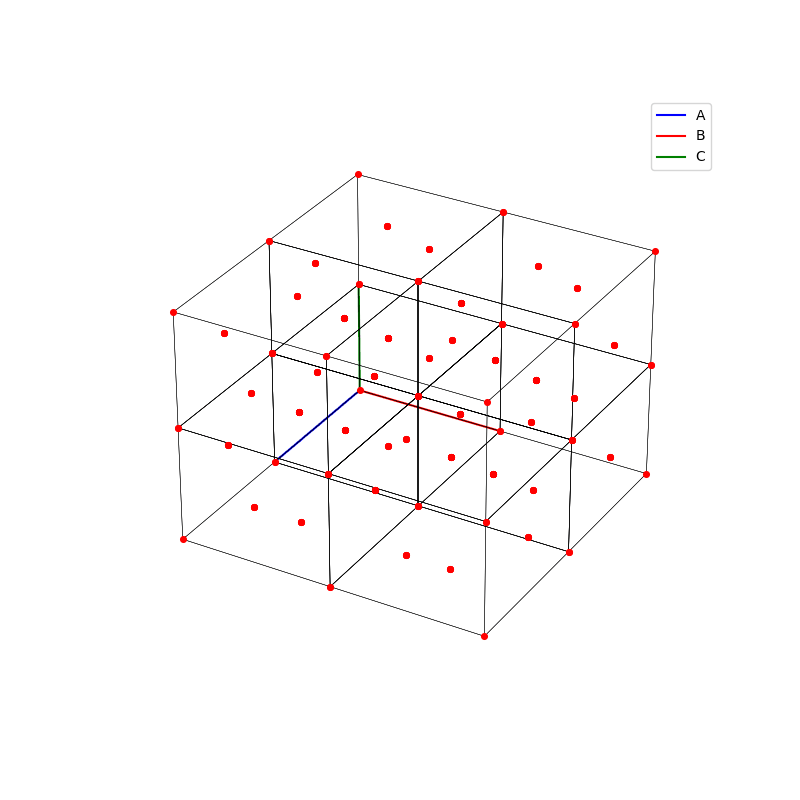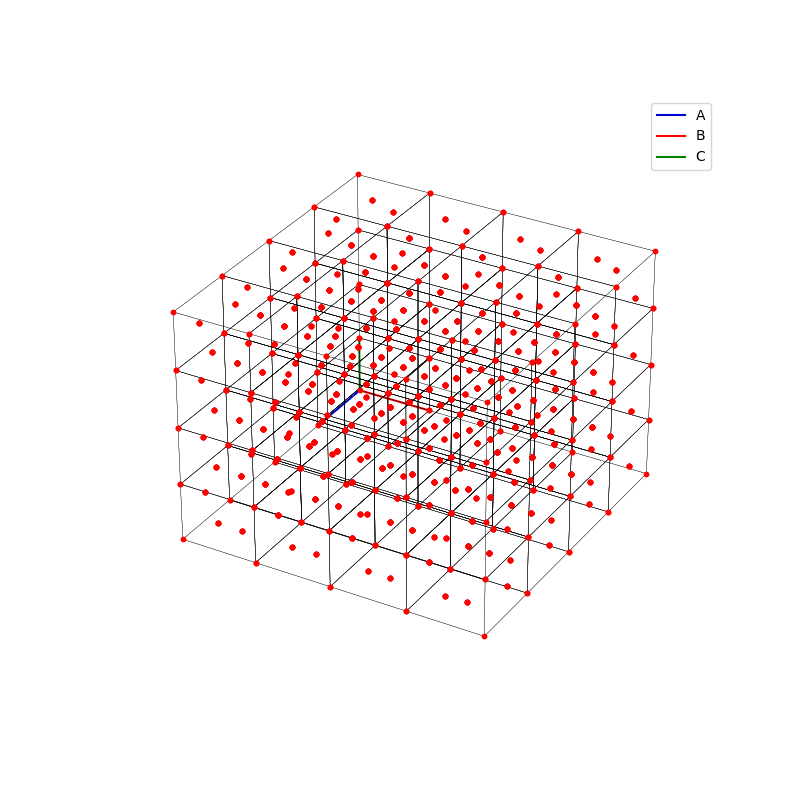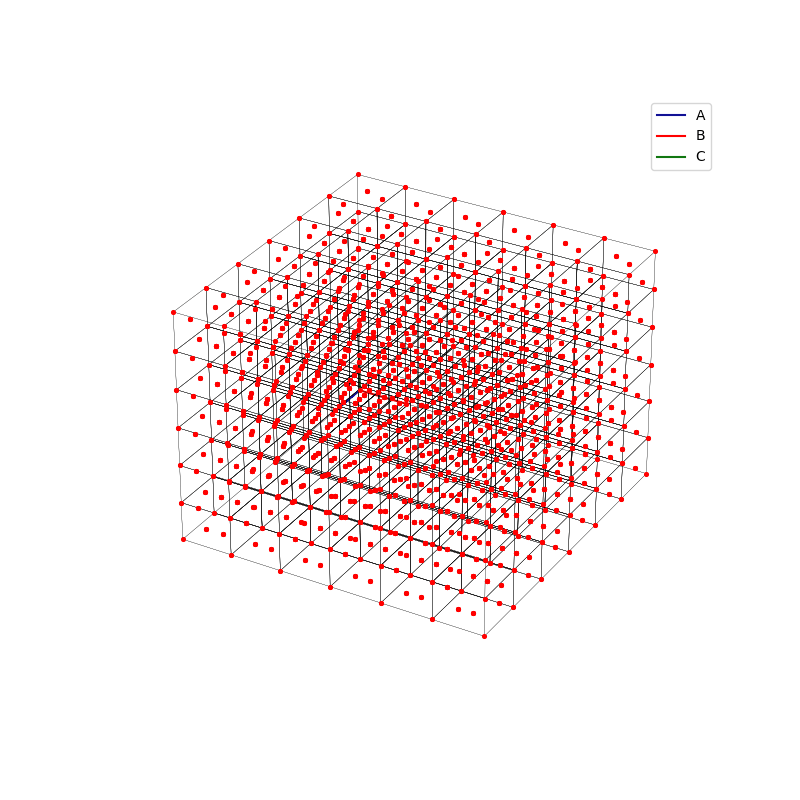
fig = plt.figure(0,figsize=[8,8])
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,projection='3d')
from PyCrystallography import unit_cell
prim = unit_cell.NaCl(ax)
fig = plt.figure(1,figsize=[8,8])
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,projection='3d')
from PyCrystallography import lattice
lattice.make_lattice_3d(ax,prim)
plt.show()
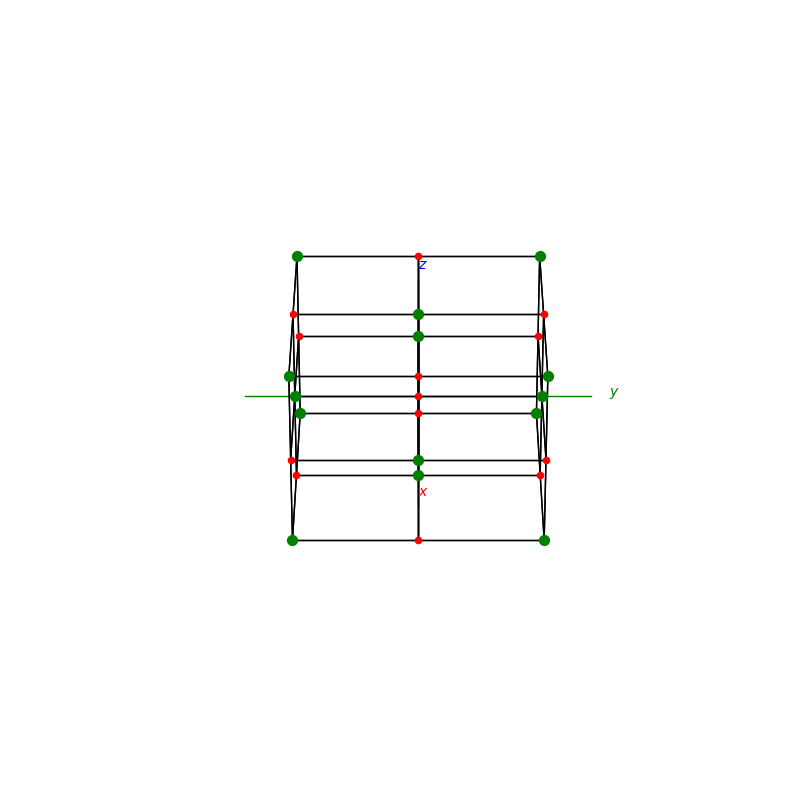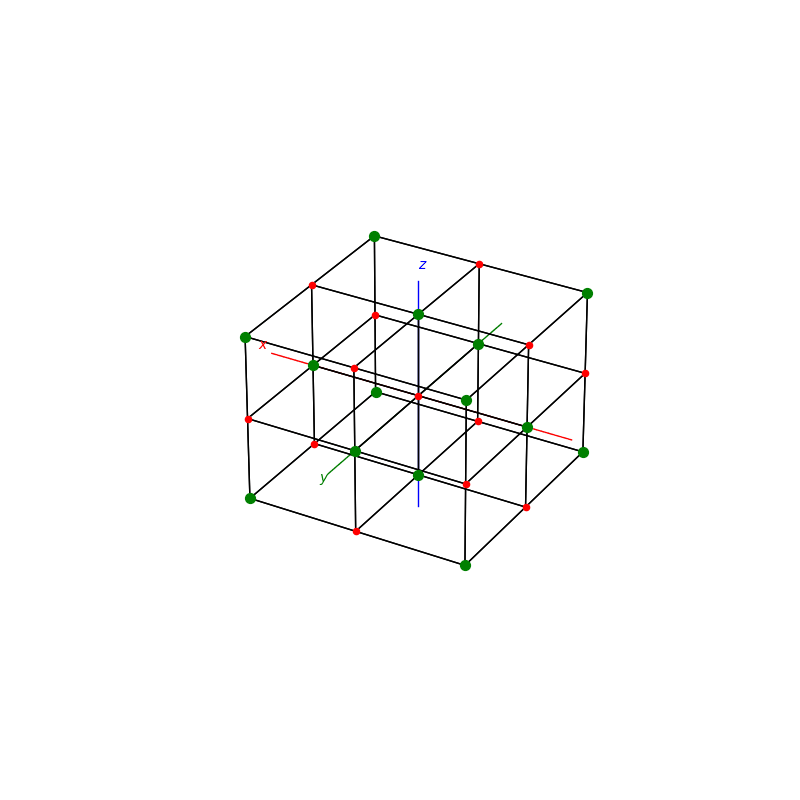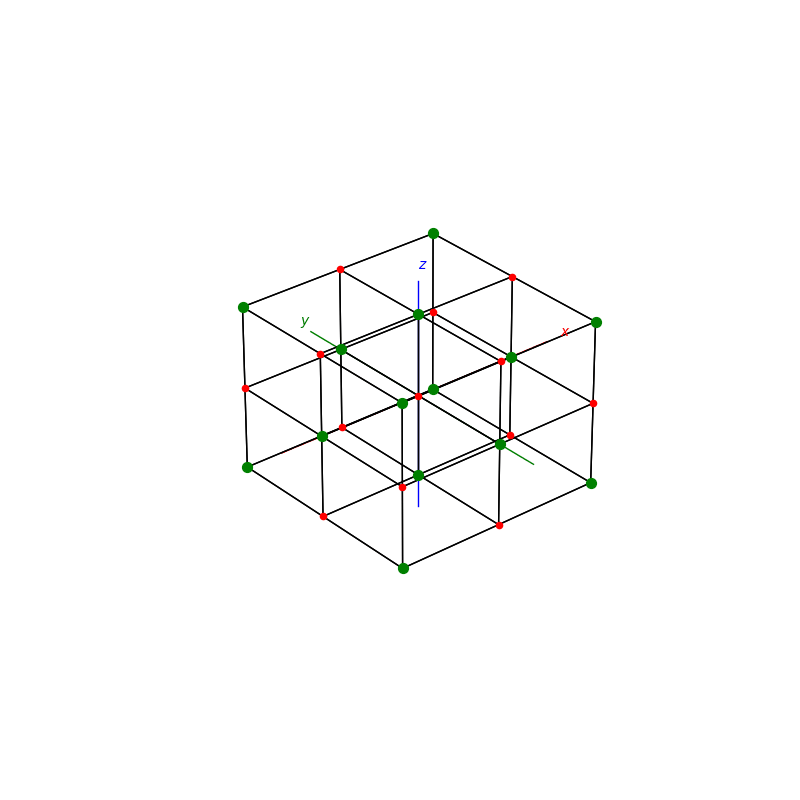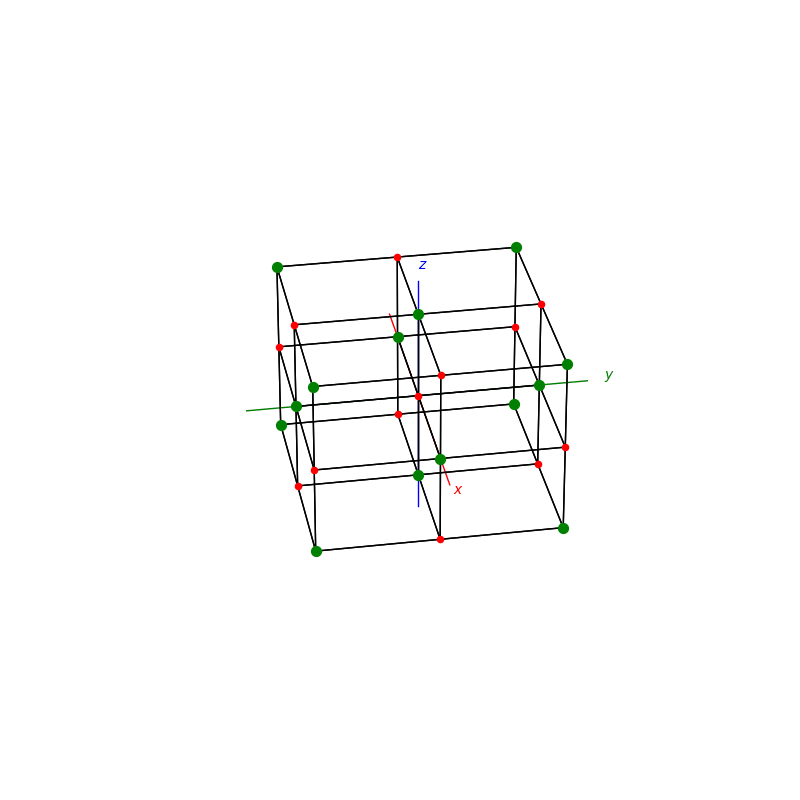
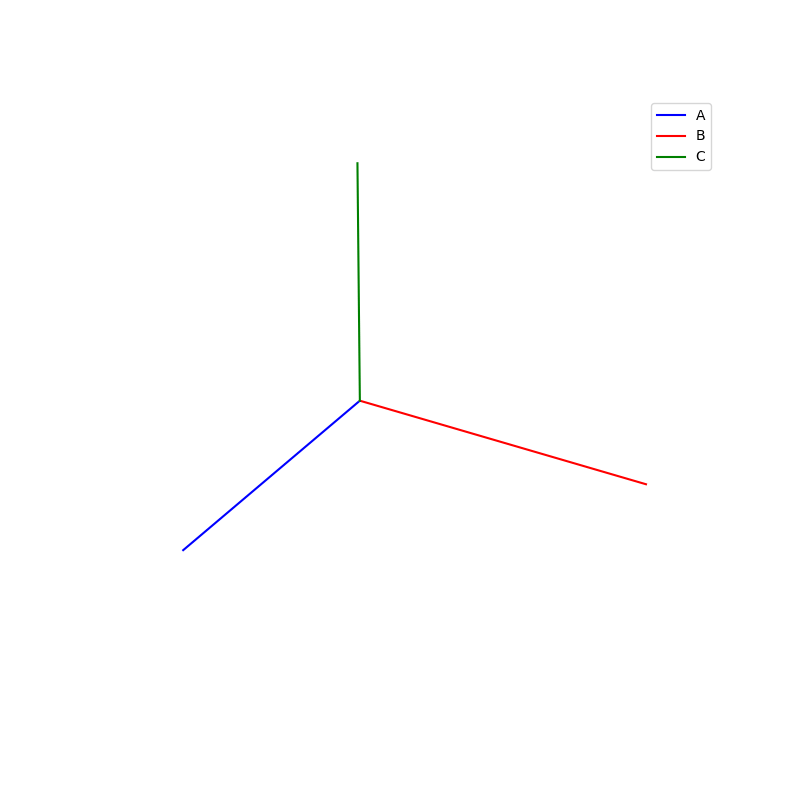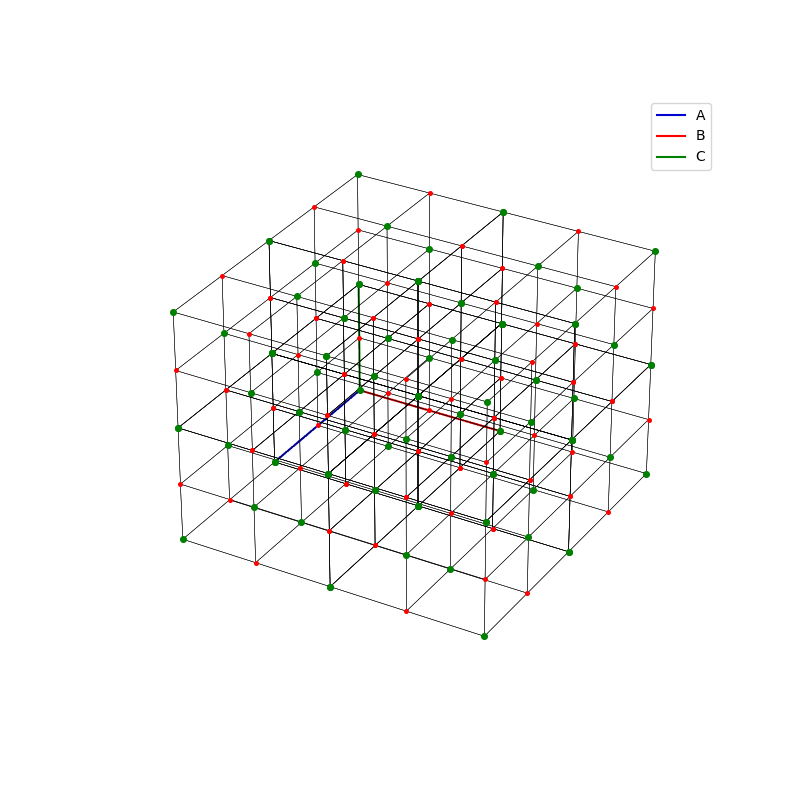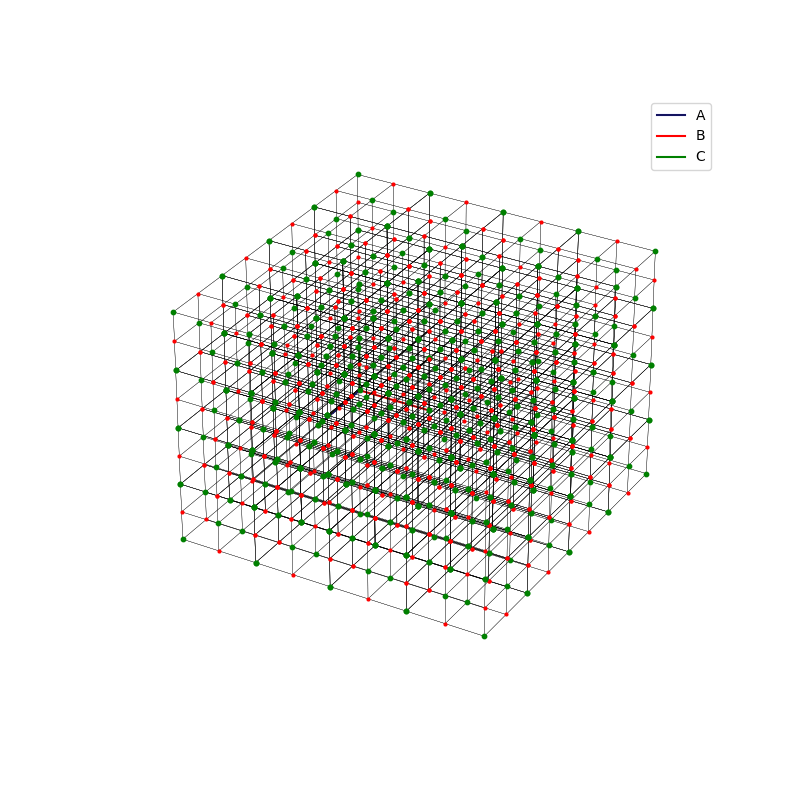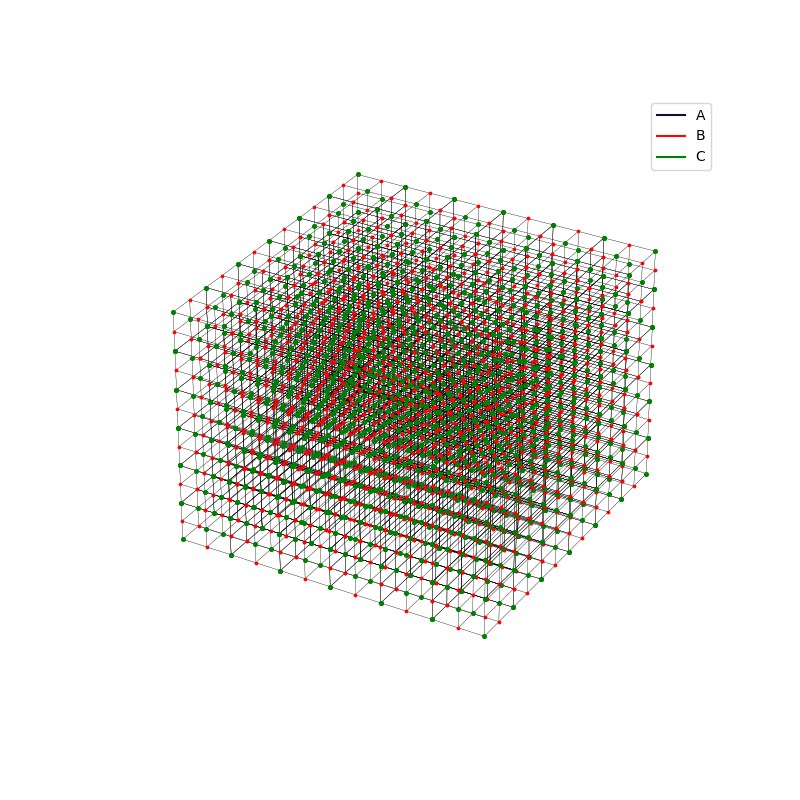
fig = plt.figure(0,figsize=[8,8])
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,projection='3d')
from PyCrystallography import unit_cell
prim = unit_cell.Diamond(ax)
fig = plt.figure(1,figsize=[8,8])
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,projection='3d')
from PyCrystallography import lattice
lattice.make_lattice_3d(ax,prim)
plt.show()
Penrose_Tiling(n,'sun')
Penrose_Tiling(n,'star')
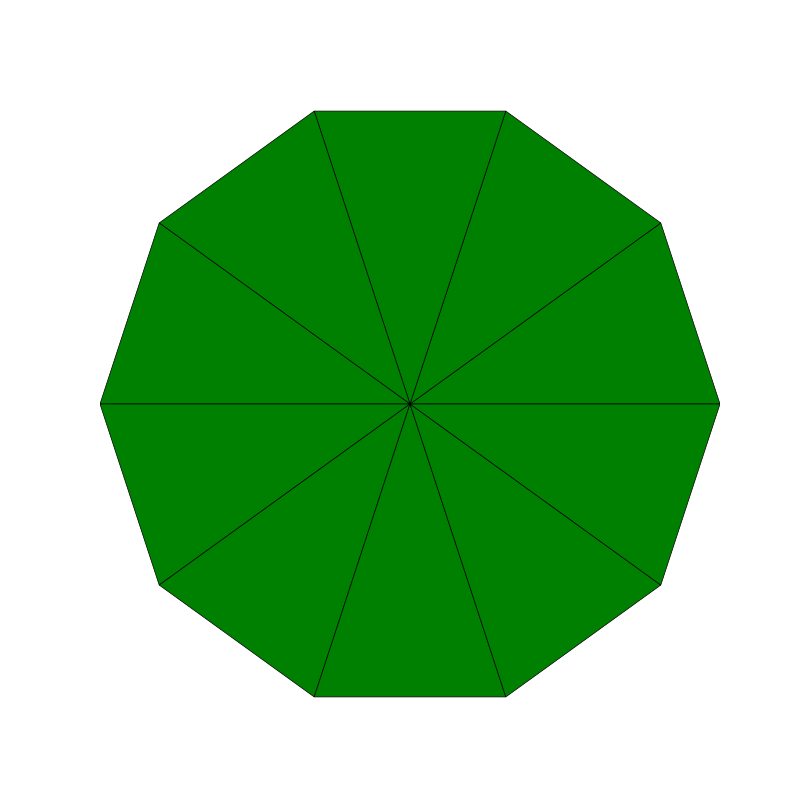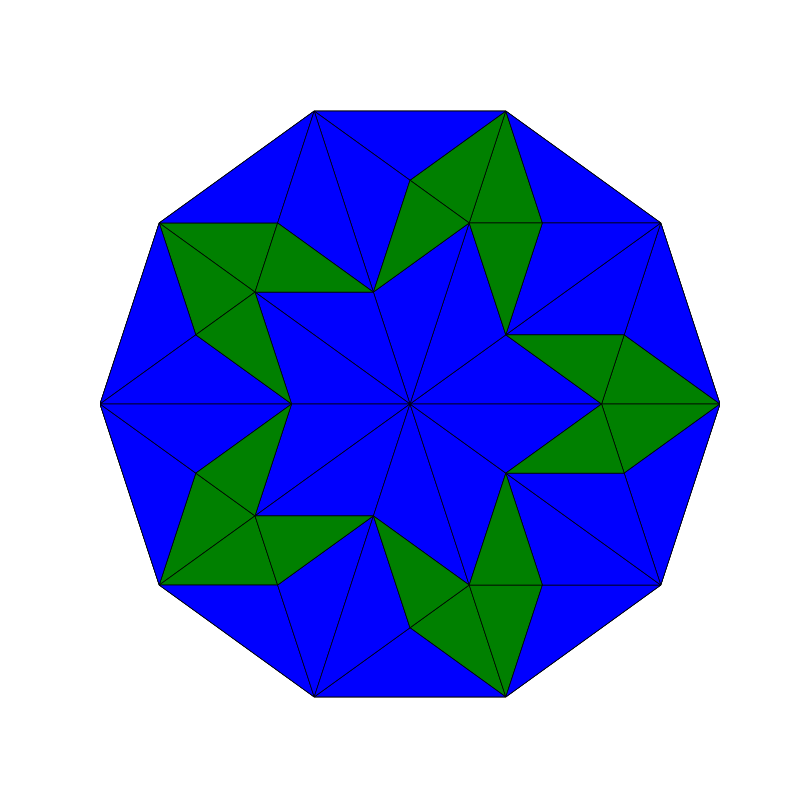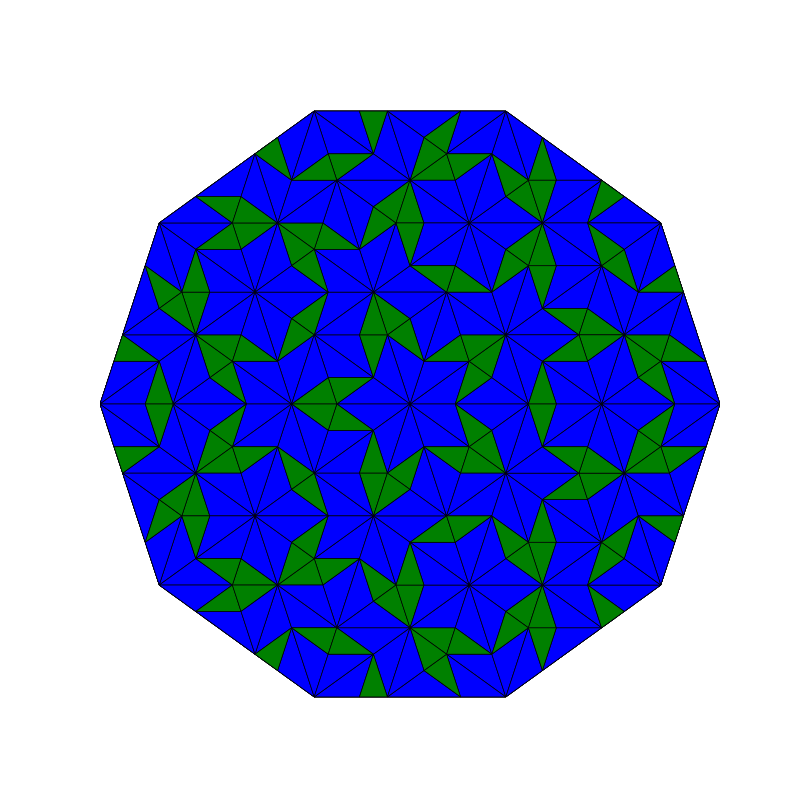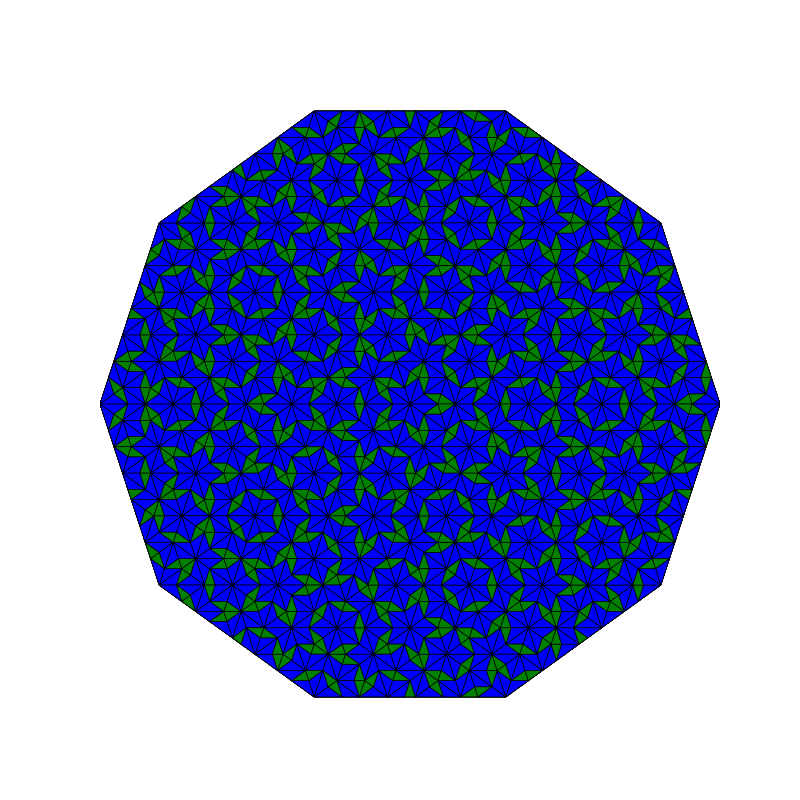
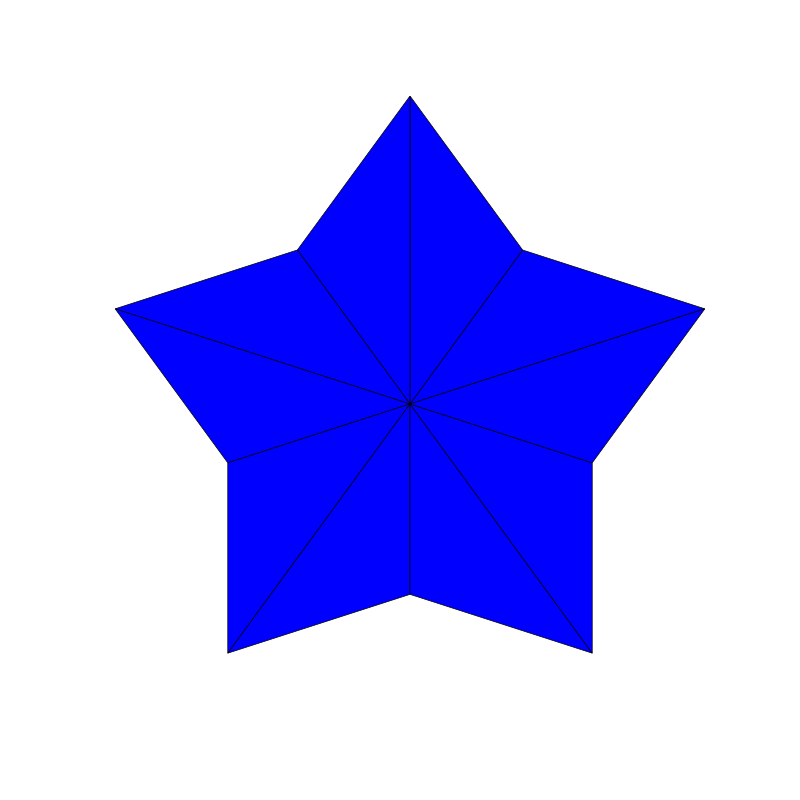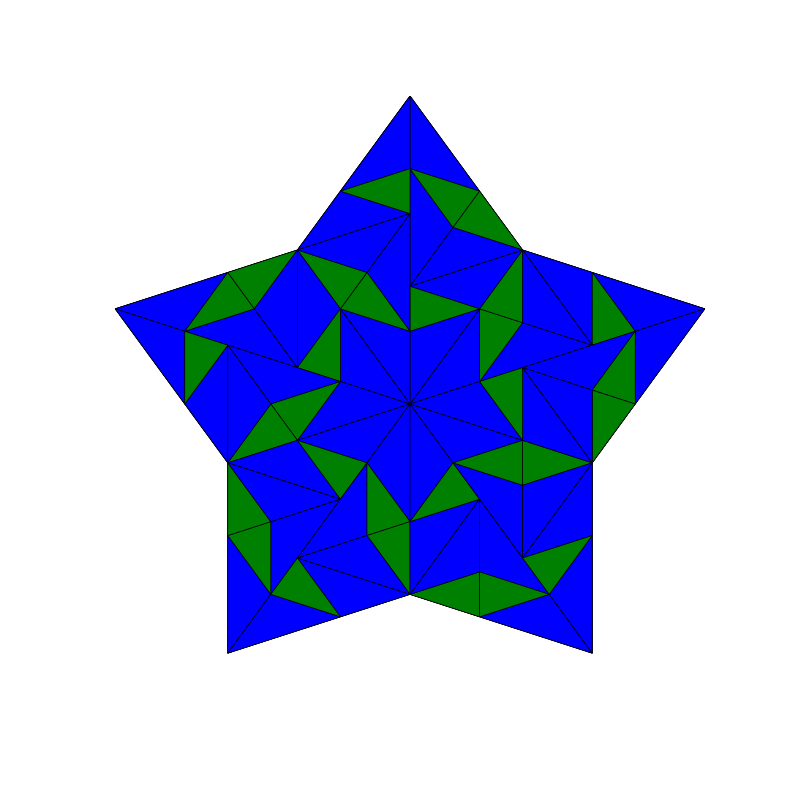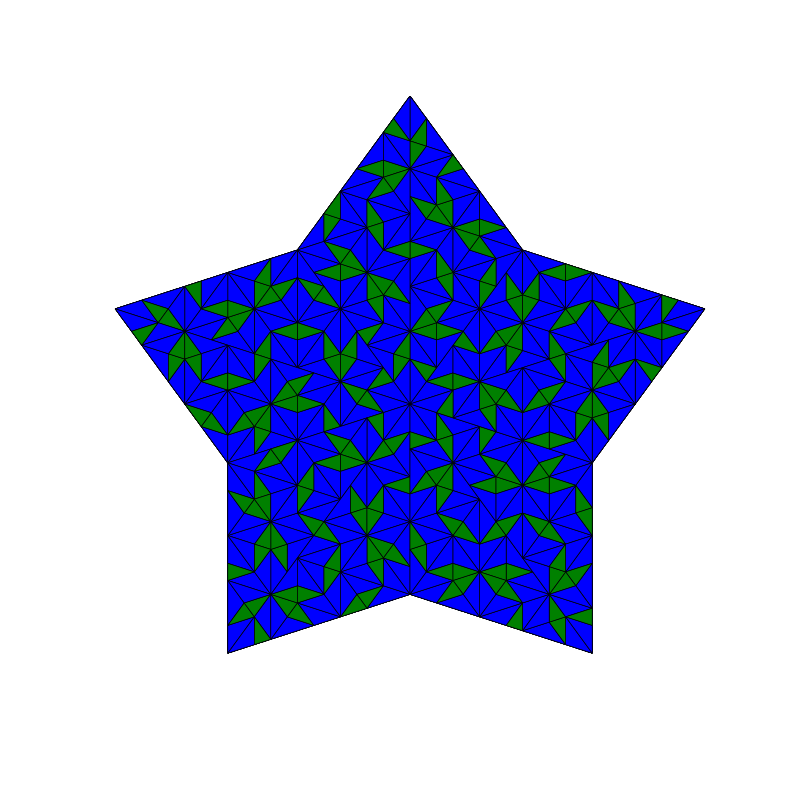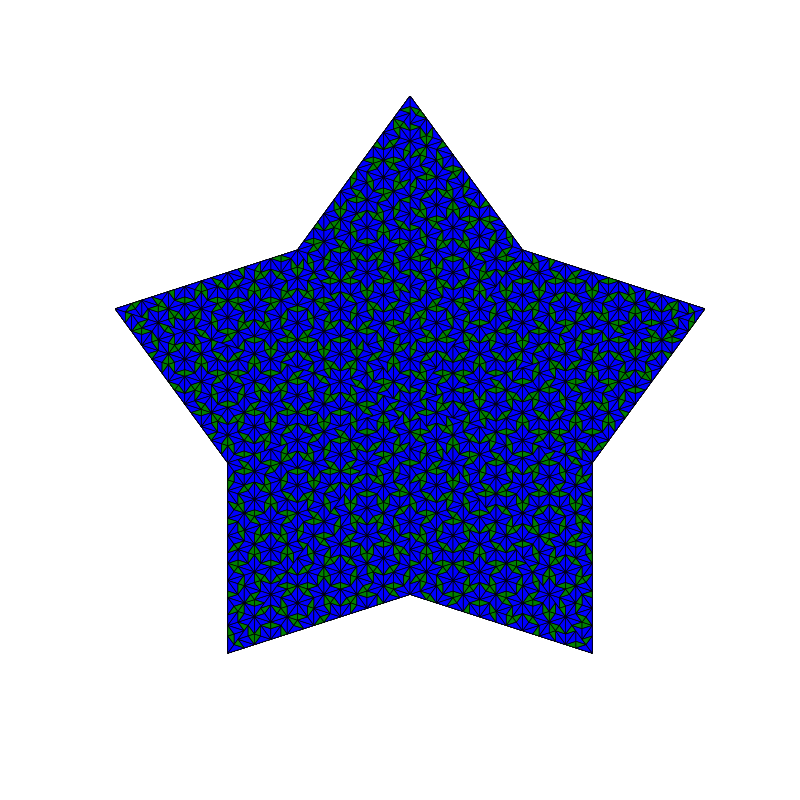
triangle_subdivision(n,'diag')
triangle_subdivision(n,'grid')
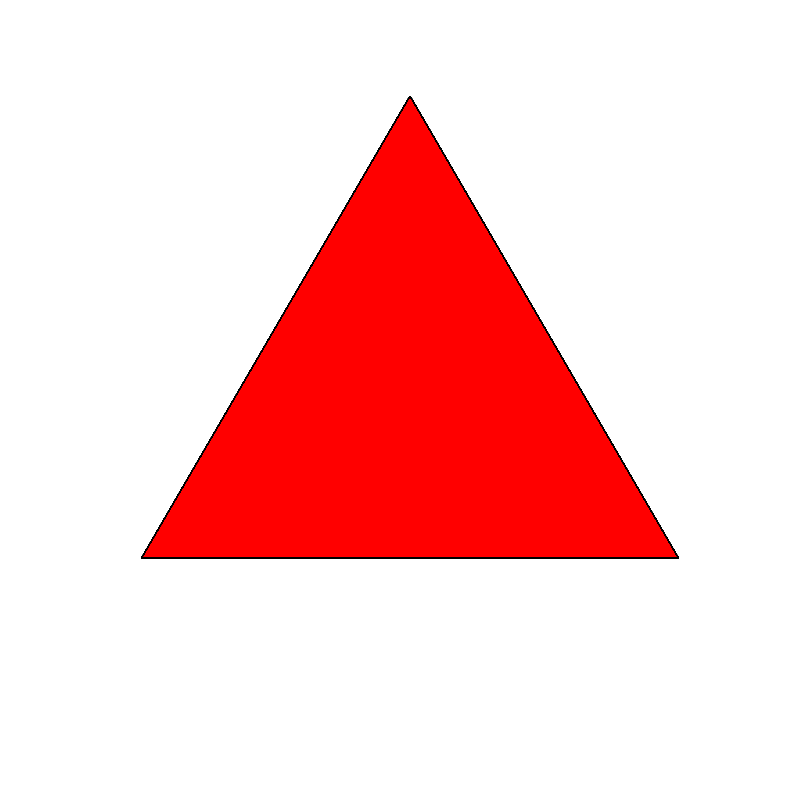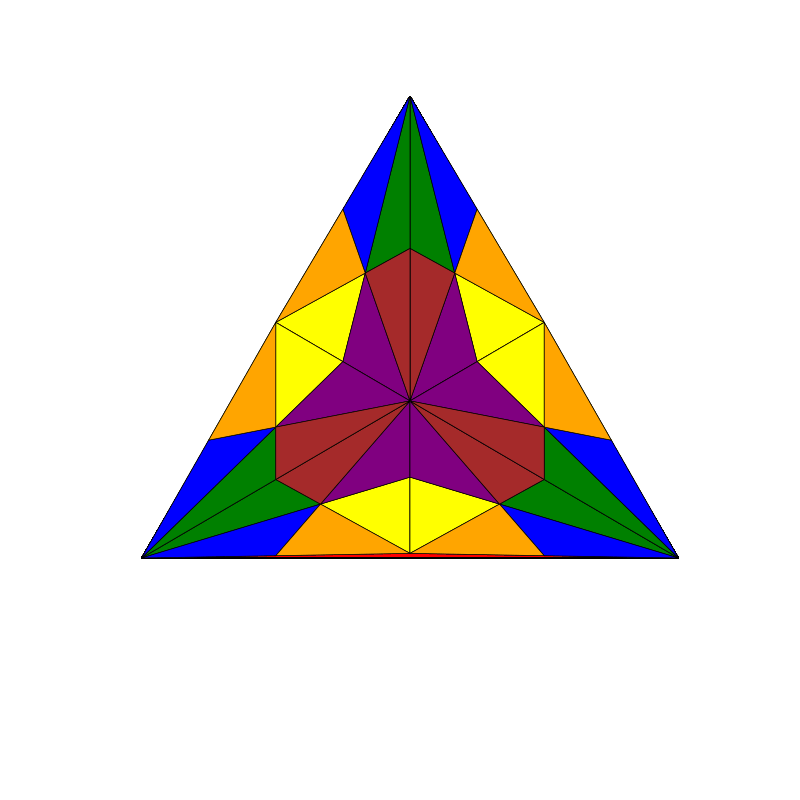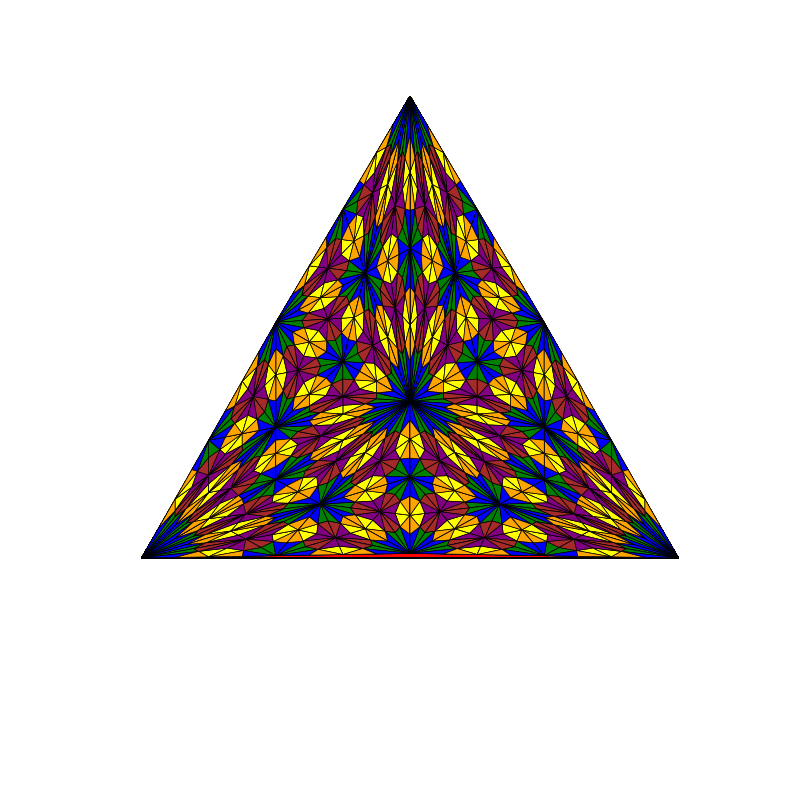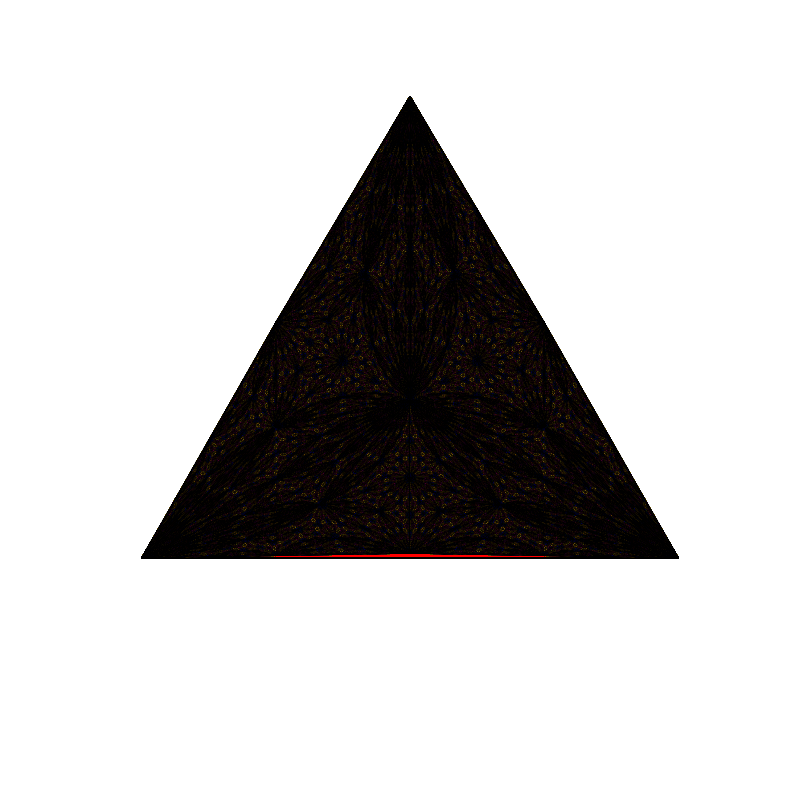

|
|
serpinksi_pyramid(n)
|
|
|
menger_cube(n)
|